Series of squares Prove that if ∑aₖ is a convergent series of positive terms, then the series ∑aₖ² also converges.
Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 55m
- Introduction to Functions18m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms36m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals4h 44m
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals2h 27m
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals 3h 16m
- 11. Integrals of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 31m
- 12. Techniques of Integration7h 41m
- 13. Intro to Differential Equations2h 55m
- 14. Sequences & Series5h 36m
- 15. Power Series2h 19m
- 16. Parametric Equations & Polar Coordinates7h 58m
14. Sequences & Series
Convergence Tests
Problem 10.7.87a
Textbook Question
Explain why or why not
Determine whether the following statements are true and give an explanation or counterexample.
a. If the Limit Comparison Test can be applied successfully to a given series with a certain comparison series, the Comparison Test also works with the same comparison series.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Recall the definitions of the Comparison Test and the Limit Comparison Test for series convergence: The Comparison Test requires that the terms of the given series and the comparison series satisfy an inequality for all sufficiently large indices, while the Limit Comparison Test uses the limit of the ratio of their terms as the index approaches infinity.
For the Comparison Test, you need to find a comparison series \( \sum b_n \) such that either \( 0 \leq a_n \leq b_n \) or \( 0 \leq b_n \leq a_n \) for all \( n \) beyond some index, and then use the known convergence or divergence of \( \sum b_n \) to conclude about \( \sum a_n \).
For the Limit Comparison Test, you compute \( \lim_{n \to \infty} \frac{a_n}{b_n} = c \), where \( c \) is a finite positive number. If this limit exists and is positive and finite, then both series either converge or diverge together.
Consider that the Limit Comparison Test can succeed even if the inequality required for the Comparison Test does not hold for all large \( n \). This means the Comparison Test might fail to apply with the same comparison series even though the Limit Comparison Test works.
Therefore, the statement is false: the successful application of the Limit Comparison Test with a certain comparison series does not guarantee that the Comparison Test will also work with the same comparison series. A counterexample can be constructed where the limit of the ratio exists and is positive, but the inequality needed for the Comparison Test fails.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
5mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Limit Comparison Test
The Limit Comparison Test determines the convergence or divergence of a series by comparing it to a second series with known behavior. It involves taking the limit of the ratio of their terms; if the limit is a positive finite number, both series either converge or diverge together.
Recommended video:
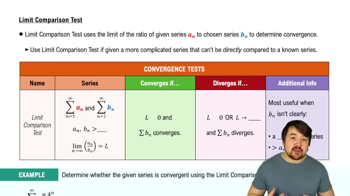
Limit Comparison Test
Comparison Test
The Comparison Test assesses a series' convergence by directly comparing its terms to those of a known convergent or divergent series. If the terms of the original series are smaller than a convergent series, it converges; if larger than a divergent series, it diverges.
Recommended video:
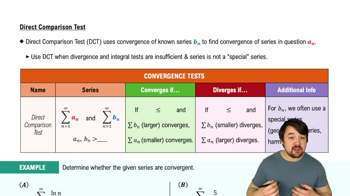
Direct Comparison Test
Differences Between Limit Comparison and Comparison Tests
While both tests compare series, the Comparison Test requires strict inequalities between terms, which can be restrictive. The Limit Comparison Test is more flexible, relying on the limit of term ratios, so it can succeed even when direct inequalities needed for the Comparison Test do not hold.
Recommended video:

Limit Comparison Test

 5:44m
5:44mWatch next
Master Divergence Test (nth Term Test) with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
23
views
