The terms of a sequence of partial sums are defined by Sₙ = ∑ⁿₖ₌₁ k² , for n=1, 2, 3, .....Evaluate the first four terms of the sequence.
Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 55m
- Introduction to Functions18m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms36m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals4h 44m
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals2h 27m
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals 3h 16m
- 11. Integrals of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 31m
- 12. Techniques of Integration7h 41m
- 13. Intro to Differential Equations2h 55m
- 14. Sequences & Series5h 36m
- 15. Power Series2h 19m
- 16. Parametric Equations & Polar Coordinates7h 58m
14. Sequences & Series
Sequences
Problem 10.1.17
Textbook Question
13–20. Explicit formulas Write the first four terms of the sequence { aₙ }∞ₙ₌₁.
aₙ = (2ⁿ⁺¹) / (2ⁿ + 1)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the given explicit formula for the sequence: \(a_n = \frac{2^{n+1}}{2^n + 1}\).
Understand that to find the first four terms, you need to substitute \(n = 1, 2, 3, 4\) into the formula.
Calculate the first term by substituting \(n=1\): \(a_1 = \frac{2^{1+1}}{2^1 + 1} = \frac{2^2}{2 + 1}\).
Calculate the second term by substituting \(n=2\): \(a_2 = \frac{2^{2+1}}{2^2 + 1} = \frac{2^3}{4 + 1}\).
Similarly, calculate the third and fourth terms by substituting \(n=3\) and \(n=4\) into the formula, respectively.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Sequences and Terms
A sequence is an ordered list of numbers defined by a specific rule or formula. Each number in the sequence is called a term, denoted as aₙ, where n indicates the term's position. Understanding how to find terms using the explicit formula is essential for generating the sequence.
Recommended video:
Guided course
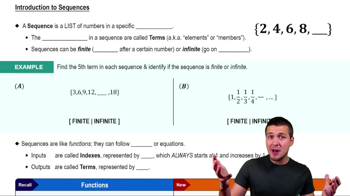
Introduction to Sequences
Explicit Formula for Sequences
An explicit formula expresses the nth term of a sequence directly in terms of n, allowing calculation of any term without knowing previous terms. For example, aₙ = (2ⁿ⁺¹) / (2ⁿ + 1) gives a direct way to find the nth term by substituting n.
Recommended video:
Guided course
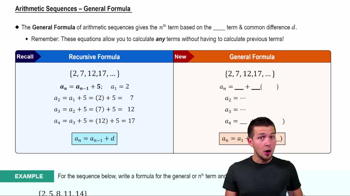
Arithmetic Sequences - General Formula
Evaluating Exponential Expressions
Evaluating terms in the sequence requires calculating powers of 2, such as 2ⁿ and 2ⁿ⁺¹. Understanding how to compute and simplify exponential expressions is crucial to accurately determine each term's value.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Simplifying Exponential Expressions

 8:22m
8:22mWatch next
Master Introduction to Sequences with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
31
views
