The Greatest and Least Integer Functions
For what values of x is
b. ⌈x⌉ = 0
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: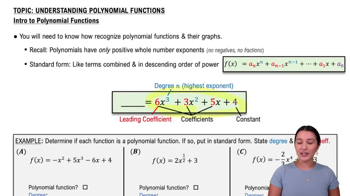
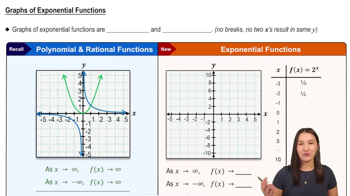


 5:57m
5:57mMaster Graphs of Common Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning