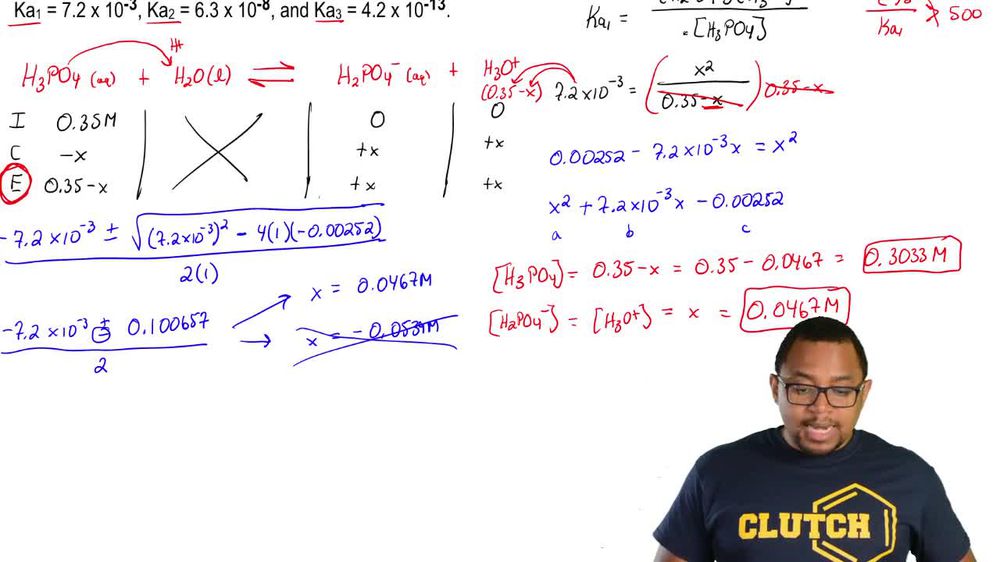Table of contents
- 1. Chemical Measurements1h 50m
- 2. Tools of the Trade1h 17m
- 3. Experimental Error1h 52m
- 4 & 5. Statistics, Quality Assurance and Calibration Methods1h 57m
- 6. Chemical Equilibrium3h 41m
- 7. Activity and the Systematic Treatment of Equilibrium1h 0m
- 8. Monoprotic Acid-Base Equilibria1h 53m
- 9. Polyprotic Acid-Base Equilibria2h 17m
- 10. Acid-Base Titrations2h 37m
- 11. EDTA Titrations1h 34m
- 12. Advanced Topics in Equilibrium1h 16m
- 13. Fundamentals of Electrochemistry2h 19m
- 14. Electrodes and Potentiometry41m
- 15. Redox Titrations1h 14m
- 16. Electroanalytical Techniques57m
- 17. Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry50m
9. Polyprotic Acid-Base Equilibria
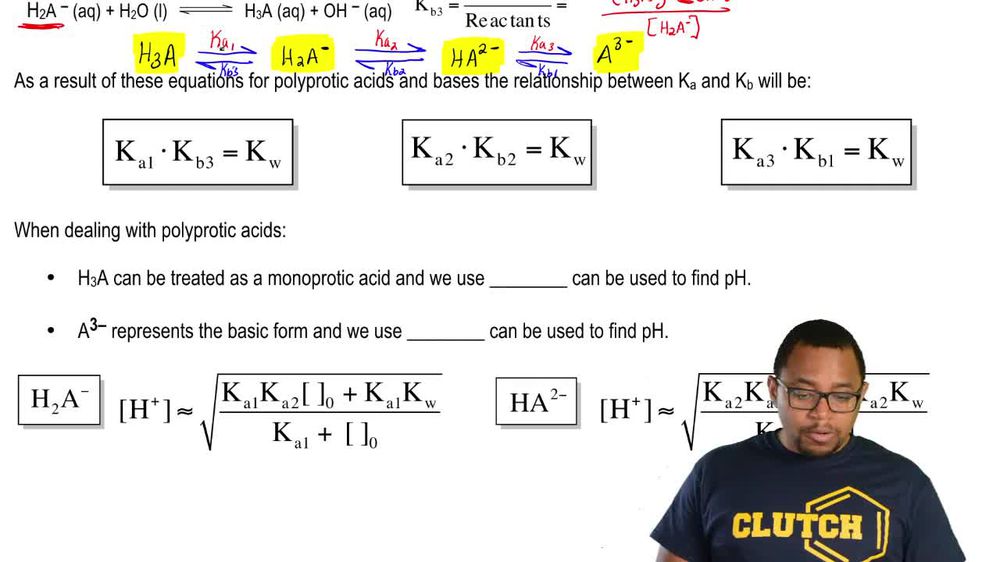
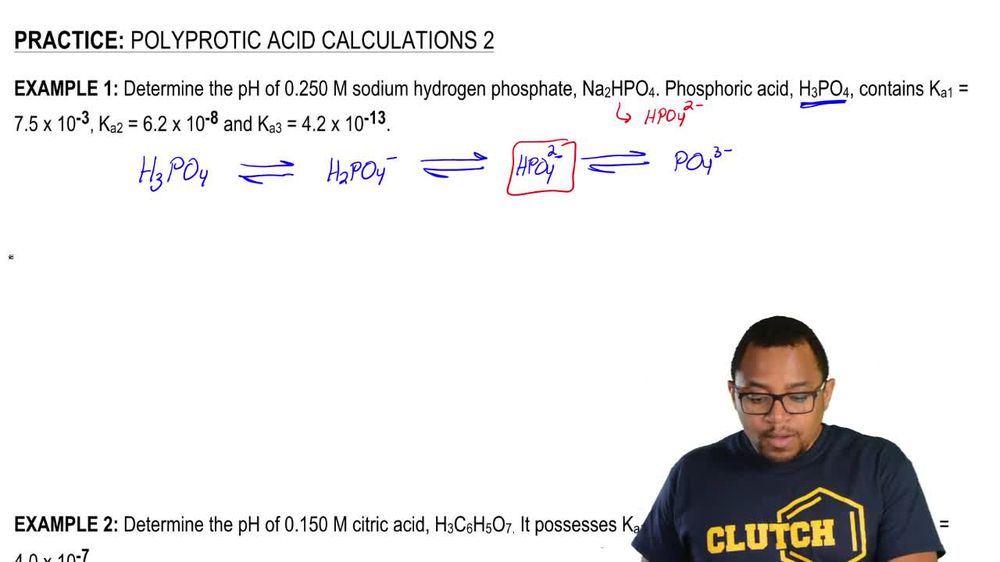
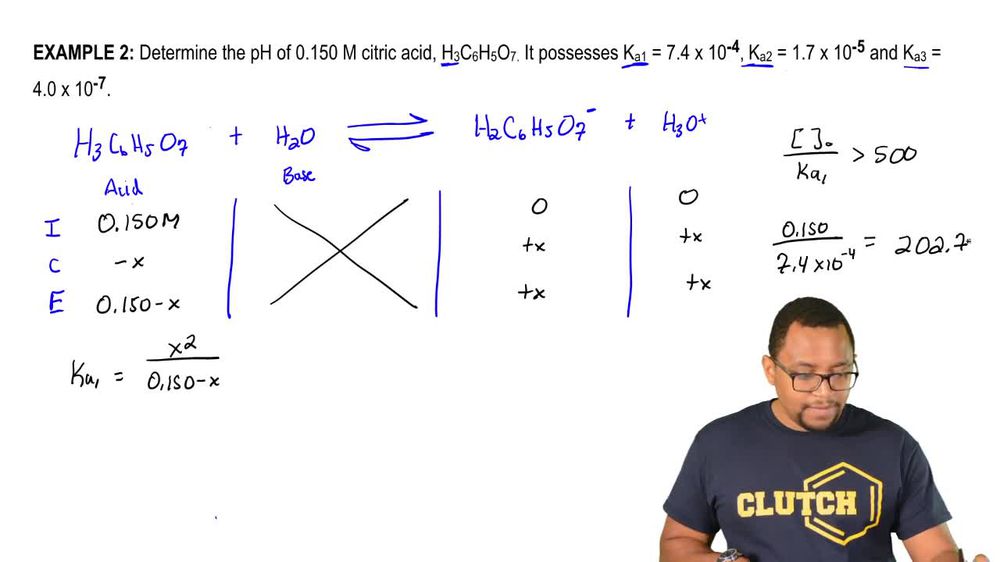
Polyprotic Acids and Bases

Polyprotic Bases
Jules Bruno
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Related Videos
Related Practice