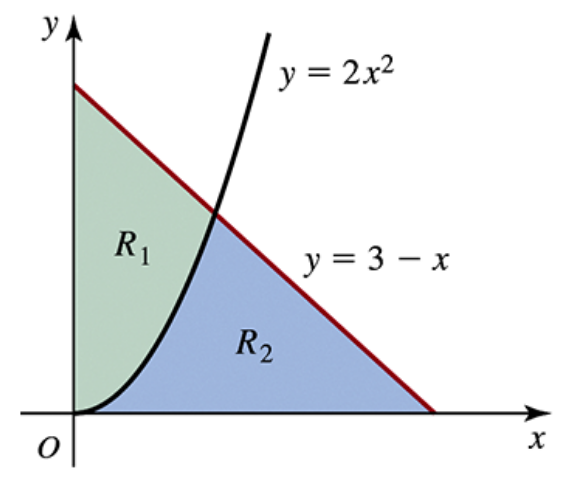
Determine the area of the shaded region in the following figures.
Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 55m
- Introduction to Functions18m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms36m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals4h 44m
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals2h 27m
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals 3h 16m
- 11. Integrals of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 31m
- 12. Techniques of Integration7h 41m
- 13. Intro to Differential Equations2h 55m
- 14. Sequences & Series5h 36m
- 15. Power Series2h 19m
- 16. Parametric Equations & Polar Coordinates7h 58m
9. Graphical Applications of Integrals
Area Between Curves
Problem 6.2.34a
Textbook Question
For the given regions R₁ and R₂, complete the following steps.
a. Find the area of region R₁.
R₁ is the region in the first quadrant bounded by the y-axis and the curves y=2x^2 and y=3−x; R₂ is the region in the first quadrant bounded by the x-axis and the curves y=2x^2 and y=3−x(see figure).
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Identify the boundaries of region R₁. Region R₁ is bounded by the y-axis (x = 0), the curve y = 2x², and the line y = 3 − x. To find the area, we need to determine the points of intersection between y = 2x² and y = 3 − x.
Step 2: Solve for the points of intersection by equating the two equations: 2x² = 3 − x. Rearrange this into a standard quadratic form: 2x² + x − 3 = 0. Use the quadratic formula or factorization to find the values of x where the curves intersect.
Step 3: Set up the integral to calculate the area of R₁. The area is given by the integral of the top curve minus the bottom curve over the interval determined by the points of intersection. Specifically, the integral is: ∫[0, x₁] ((3 − x) − (2x²)) dx, where x₁ is the x-coordinate of the intersection point.
Step 4: Break down the integral into simpler components. Expand the integrand: (3 − x − 2x²). Compute the integral term by term: ∫[0, x₁] 3 dx, ∫[0, x₁] −x dx, and ∫[0, x₁] −2x² dx.
Step 5: Evaluate each integral over the interval [0, x₁] and combine the results to find the total area of region R₁. This will give the area enclosed by the curves and the y-axis.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
5mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Definite Integrals
Definite integrals are used to calculate the area under a curve between two points on the x-axis. In this context, the area of region R₁ can be found by integrating the difference between the upper curve (y = 3 - x) and the lower curve (y = 2x²) over the interval defined by their intersection points. This process quantifies the total area enclosed by the curves.
Recommended video:

Definition of the Definite Integral
Finding Intersection Points
To determine the area of region R₁, it is essential to find the intersection points of the curves y = 2x² and y = 3 - x. These points are where the two curves meet, and they define the limits of integration for calculating the area. Solving the equation 2x² = 3 - x will yield the x-values at which the curves intersect.
Recommended video:

Critical Points
Area Between Curves
The area between two curves is calculated by integrating the difference of the functions that define the curves over a specified interval. For region R₁, the area can be expressed as the integral of (3 - x - 2x²) dx, evaluated from the left intersection point to the right intersection point. This method effectively captures the space between the two curves.
Recommended video:
Finding Area Between Curves on a Given Interval

 5:23m
5:23mWatch next
Master Finding Area Between Curves on a Given Interval with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
36
views
