Area of region Find the area of the region bounded by y = sech x, x = 1, and the unit circle (see figure).
Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 55m
- Introduction to Functions18m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms36m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals4h 44m
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals2h 27m
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals 3h 16m
- 11. Integrals of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 31m
- 12. Techniques of Integration7h 41m
- 13. Intro to Differential Equations2h 55m
- 14. Sequences & Series5h 36m
- 15. Power Series2h 19m
- 16. Parametric Equations & Polar Coordinates7h 58m
11. Integrals of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions
Integrals Involving Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Problem 7.3.59a
Textbook Question
Visual approximation
a. Use a graphing utility to sketch the graph of y = coth x and then explain why ∫₅¹⁰ coth x dx ≈ 5.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Recall the definition of the hyperbolic cotangent function: \(y = \coth x = \frac{\cosh x}{\sinh x}\), where \(\sinh x\) and \(\cosh x\) are the hyperbolic sine and cosine functions respectively.
Use a graphing utility to plot the function \(y = \coth x\) over the interval \([5, 10]\). Observe the behavior of the graph in this range, noting that \(\coth x\) approaches 1 as \(x\) becomes large.
Understand that the definite integral \(\int_5^{10} \coth x \, dx\) represents the area under the curve of \(y = \coth x\) from \(x=5\) to \(x=10\).
Since \(\coth x\) is close to 1 for large \(x\), the graph between 5 and 10 is near the horizontal line \(y=1\). Therefore, the area under the curve is approximately the area of a rectangle with height 1 and width \$10 - 5 = 5$.
Conclude that this approximation explains why \(\int_5^{10} \coth x \, dx \approx 5\), because the integral sums values close to 1 over an interval of length 5.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Hyperbolic Cotangent Function (coth x)
The hyperbolic cotangent function, coth x, is defined as cosh x divided by sinh x. It behaves similarly to the reciprocal of the tangent function but for hyperbolic angles. Understanding its shape and asymptotic behavior helps in visualizing the graph and estimating integrals involving coth x.
Recommended video:
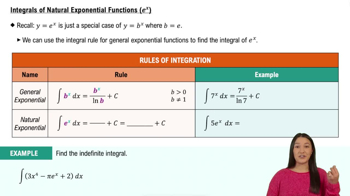
Integrals of Natural Exponential Functions (e^x)
Definite Integral as Area Under the Curve
A definite integral ∫_a^b f(x) dx represents the net area between the graph of f(x) and the x-axis from x = a to x = b. Visualizing this area on the graph of coth x allows approximation of the integral's value by estimating the region's size.
Recommended video:

Definition of the Definite Integral
Using Graphing Utilities for Approximation
Graphing utilities plot functions accurately, revealing key features like asymptotes and behavior over intervals. By sketching y = coth x from 5 to 10, one can visually assess the area under the curve, supporting an approximate value for the integral without exact calculation.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Cotangent Graph

 4:51m
4:51mWatch next
Master Integrals Resulting in Inverse Trig Functions with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
21
views
