Describe the hyperbola .
Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 55m
- Introduction to Functions18m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms36m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals4h 44m
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals2h 27m
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals 3h 16m
- 11. Integrals of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 31m
- 12. Techniques of Integration7h 41m
- 13. Intro to Differential Equations2h 55m
- 14. Sequences & Series5h 36m
- 15. Power Series2h 19m
- 16. Parametric Equations & Polar Coordinates7h 58m
16. Parametric Equations & Polar Coordinates
Conic Sections
Problem 12.4.31
Textbook Question
31–38. Equations of parabolas Find an equation of the following parabolas. Unless otherwise specified, assume the vertex is at the origin.
A parabola that opens to the right with directrix x = -4
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Recall the definition of a parabola: it is the set of all points equidistant from the focus and the directrix.
Since the directrix is given as the vertical line \(x = -4\) and the parabola opens to the right, the axis of symmetry is horizontal along the x-axis.
The vertex is at the origin \((0,0)\), so the focus must be on the positive x-axis, at some point \((p,0)\), where \(p > 0\).
The distance from the vertex to the directrix is \(|p| = 4\), so the focus is at \((4,0)\).
Use the standard form of a parabola that opens right: \(y^2 = 4px\). Substitute \(p = 4\) to get the equation \(y^2 = 16x\).
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Definition of a Parabola
A parabola is the set of all points equidistant from a fixed point called the focus and a fixed line called the directrix. This geometric definition helps derive the equation of the parabola by relating distances from any point on the curve to the focus and directrix.
Recommended video:

Definition of the Definite Integral
Orientation of Parabolas
The orientation of a parabola depends on the position of its focus and directrix. If the parabola opens right or left, its axis of symmetry is horizontal, and the equation involves x and y accordingly. For a parabola opening right, the directrix is vertical, and the equation typically has the form (y - k)^2 = 4p(x - h).
Recommended video:
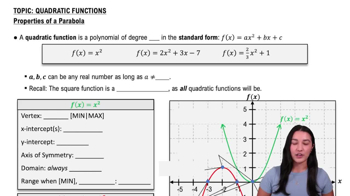
Properties of Parabolas
Vertex at the Origin and Directrix
When the vertex is at the origin, the parabola's equation simplifies since h = 0 and k = 0. Given the directrix x = -4, the focus lies on the opposite side of the vertex at x = 4, allowing calculation of the parameter p, which determines the distance from the vertex to the focus or directrix and shapes the parabola's equation.
Recommended video:
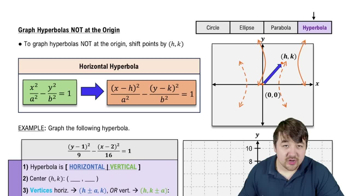
Graph Hyperbolas NOT at the Origin

 3:8m
3:8mWatch next
Master Geometries from Conic Sections with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Multiple Choice
63
views
1
rank
