Eliminate the parameter to rewrite the following as a rectangular equation.
Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 55m
- Introduction to Functions18m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms36m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals4h 44m
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals2h 27m
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals 3h 16m
- 11. Integrals of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 31m
- 12. Techniques of Integration7h 41m
- 13. Intro to Differential Equations2h 55m
- 14. Sequences & Series5h 36m
- 15. Power Series2h 19m
- 16. Parametric Equations & Polar Coordinates7h 58m
16. Parametric Equations & Polar Coordinates
Parametric Equations
Problem 12.1.13a
Textbook Question
11–14. Working with parametric equations Consider the following parametric equations.
a. Make a brief table of values of t, x, and y.
b. Plot the (x, y) pairs in the table and the complete parametric curve, indicating the positive orientation (the direction of increasing t).
x=−t+6, y=3t−3; −5≤t≤5
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the parametric equations given: \(x = -t + 6\) and \(y = 3t - 3\), with the parameter \(t\) ranging from \(-5\) to \$5$.
Choose several values of \(t\) within the interval \([-5, 5]\). For example, select \(t = -5, -3, 0, 2, 5\) to get a good spread of points.
Calculate the corresponding \(x\) and \(y\) values for each chosen \(t\) by substituting into the parametric equations: \(x = -t + 6\) and \(y = 3t - 3\).
Create a table listing each \(t\) value alongside its calculated \(x\) and \(y\) values. This table will help visualize how the points move as \(t\) changes.
Plot the points \((x, y)\) from the table on the coordinate plane. Then, sketch the curve formed by the parametric equations over the interval \(-5 \leq t \leq 5\), indicating the direction of increasing \(t\) to show the positive orientation of the curve.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Parametric Equations
Parametric equations express the coordinates of points on a curve as functions of a parameter, usually denoted t. Instead of y as a function of x, both x and y depend on t, allowing the description of more complex curves and motions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
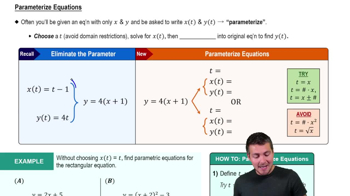
Parameterizing Equations
Creating a Table of Values
To analyze parametric equations, select values of the parameter t within the given interval, then compute corresponding x and y values. This table helps visualize points on the curve and understand how the curve evolves as t changes.
Recommended video:

Average Value of a Function
Plotting and Orientation of Parametric Curves
Plotting the (x, y) pairs from the table reveals the shape of the parametric curve. The positive orientation indicates the direction in which the curve is traced as t increases, which is important for understanding motion or direction along the curve.
Recommended video:
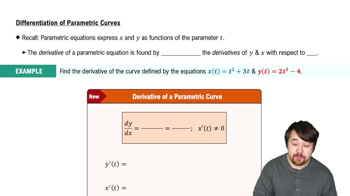
Differentiation of Parametric Curves
Related Videos
Related Practice
Multiple Choice
114
views
2
rank


