Evaluate the following limit, if it exists. If the limit does not exist, select 'DNE'.
Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 55m
- Introduction to Functions18m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms36m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals4h 44m
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals2h 27m
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals 3h 16m
- 11. Integrals of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 31m
- 12. Techniques of Integration7h 41m
- 13. Intro to Differential Equations2h 55m
- 14. Sequences & Series5h 36m
- 15. Power Series2h 19m
- 16. Parametric Equations & Polar Coordinates7h 58m
1. Limits and Continuity
Finding Limits Algebraically
Problem 7.R.29b
Textbook Question
Log-normal probability distribution A commonly used distribution in probability and statistics is the log-normal distribution. (If the logarithm of a variable has a normal distribution, then the variable itself has a log-normal distribution.) The distribution function is
f(x) = 1/xσ√(2π) e⁻ˡⁿ^² ˣ / ²σ^², for x ≥ 0
where ln x has zero mean and standard deviation σ > 0.
b. Evaluate lim x → 0 ƒ(x). (Hint: Let x = eʸ.)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Start by writing down the given probability density function (pdf) for the log-normal distribution:
\(f(x) = \frac{1}{x \sigma \sqrt{2\pi}} e^{-\frac{(\ln x)^2}{2 \sigma^2}}\), for \(x \geq 0\).
To evaluate the limit as \(x\) approaches 0, use the hint and substitute \(x = e^y\). This means as \(x \to 0^+\), we have \(y = \ln x \to -\infty\).
Rewrite the function in terms of \(y\):
\(f(e^y) = \frac{1}{e^y \sigma \sqrt{2\pi}} e^{-\frac{y^2}{2 \sigma^2}} = \frac{1}{\sigma \sqrt{2\pi}} e^{-y} e^{-\frac{y^2}{2 \sigma^2}}\).
Combine the exponents to get a single exponential expression:
\(f(e^y) = \frac{1}{\sigma \sqrt{2\pi}} e^{-y - \frac{y^2}{2 \sigma^2}}\).
Analyze the behavior of the exponent \(-y - \frac{y^2}{2 \sigma^2}\) as \(y \to -\infty\). This will help determine the limit of \(f(x)\) as \(x \to 0^+\).
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Log-normal Distribution
A log-normal distribution describes a random variable whose logarithm is normally distributed. If Y = ln(X) follows a normal distribution, then X is log-normally distributed. This distribution is skewed and only defined for positive values, commonly used in modeling multiplicative processes.
Recommended video:
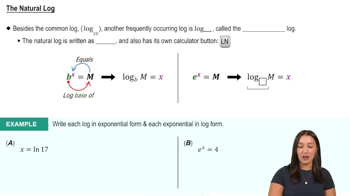
The Natural Log
Limit Evaluation Using Substitution
Evaluating limits involving complex functions often requires substitution to simplify the expression. Here, substituting x = e^y transforms the limit as x approaches 0 into a limit as y approaches -∞, making it easier to analyze the behavior of the function near zero.
Recommended video:

Finding Limits by Direct Substitution
Behavior of Exponential and Logarithmic Functions at Infinity
Understanding how exponential and logarithmic functions behave as their arguments approach infinity or negative infinity is crucial. For example, e^y approaches 0 as y → -∞, and ln(x) approaches -∞ as x → 0+, which helps in evaluating limits involving these functions.
Recommended video:
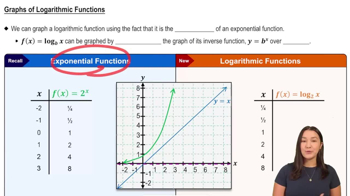
Graphs of Logarithmic Functions
Related Videos
Related Practice
Multiple Choice
53
views


