Determine if the graph of the function is continuous and/or differentiable at .
Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 55m
- Introduction to Functions18m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms36m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals4h 44m
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals2h 27m
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals 3h 16m
- 11. Integrals of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 31m
- 12. Techniques of Integration7h 41m
- 13. Intro to Differential Equations2h 55m
- 14. Sequences & Series5h 36m
- 15. Power Series2h 19m
- 16. Parametric Equations & Polar Coordinates7h 58m
2. Intro to Derivatives
Differentiability
Multiple Choice
Determine if the functionf(x) is continuous and/or differentiable at x=3.
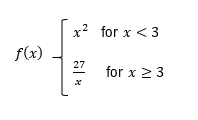
A
Continuous and non-differentiable
B
Continuous and differentiable
C
Discontinuous and non-differentiable
D
Discontinuous and differentiable
2 Comments
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: To determine if the function is continuous at x=3, check if the left-hand limit, right-hand limit, and the function value at x=3 are equal. Calculate the left-hand limit as x approaches 3 from the left using f(x) = x^2.
Step 2: Calculate the right-hand limit as x approaches 3 from the right using f(x) = 27/x. Compare this limit with the left-hand limit calculated in Step 1.
Step 3: Evaluate the function value at x=3 using f(x) = 27/x. Compare this value with the limits calculated in Steps 1 and 2 to determine continuity.
Step 4: To determine differentiability at x=3, check if the derivative from the left and the derivative from the right are equal. Calculate the derivative of f(x) = x^2 at x=3 using the definition of the derivative.
Step 5: Calculate the derivative of f(x) = 27/x at x=3 using the definition of the derivative. Compare this derivative with the one calculated in Step 4 to determine differentiability.
Related Videos
Related Practice
Multiple Choice
303
views
4
rank





