Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Psychology1h 43m
- 2. Psychology Research2h 20m
- 3. Biological Psychology2h 41m
- 4. Sensation and Perception28m
- 5. Consciousness and Sleep32m
- 6. Learning1h 26m
- 7. Memory34m
- 8. Cognition37m
- 9. Emotion and Motivation35m
- 10. Developmental Psychology1h 20m
- 11. Personality1h 17m
- 12. Social Psychology1h 18m
- 13. Stress and Health41m
- 14. Psychological Disorders1h 27m
- 15. Treatment1h 24m
6. Learning
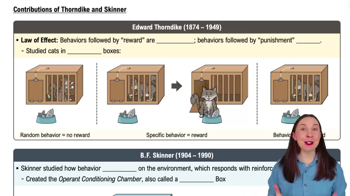
Operant Conditioning

Example 2
Hannah Gordils
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Related Videos
Related Practice