When using a change of variables u = g(𝓍) to evaluate the definite integral ∫ₐᵇ ƒ(g(𝓍)) g' (𝓍) d(𝓍), how are the limits of integration transformed?
Table of contents
- 0. Functions7h 55m
- Introduction to Functions18m
- Piecewise Functions10m
- Properties of Functions9m
- Common Functions1h 8m
- Transformations5m
- Combining Functions27m
- Exponent rules32m
- Exponential Functions28m
- Logarithmic Functions24m
- Properties of Logarithms36m
- Exponential & Logarithmic Equations35m
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions38m
- Graphs of Trigonometric Functions44m
- Trigonometric Identities47m
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions48m
- 1. Limits and Continuity2h 2m
- 2. Intro to Derivatives1h 33m
- 3. Techniques of Differentiation3h 18m
- 4. Applications of Derivatives2h 38m
- 5. Graphical Applications of Derivatives6h 2m
- 6. Derivatives of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 37m
- 7. Antiderivatives & Indefinite Integrals1h 26m
- 8. Definite Integrals4h 44m
- 9. Graphical Applications of Integrals2h 27m
- 10. Physics Applications of Integrals 3h 16m
- 11. Integrals of Inverse, Exponential, & Logarithmic Functions2h 31m
- 12. Techniques of Integration7h 41m
- 13. Intro to Differential Equations2h 55m
- 14. Sequences & Series5h 36m
- 15. Power Series2h 19m
- 16. Parametric Equations & Polar Coordinates7h 58m
8. Definite Integrals
Substitution
Problem 7.3.56
Textbook Question
37–56. Integrals Evaluate each integral.
∫₂₅²²⁵ dx / (x² + 25x) (Hint: √(x² + 25x) = √x √(x + 25).)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Start by examining the integral \( \int \frac{dx}{x^{2} + 25x} \). Notice that the denominator can be factored as \( x(x + 25) \).
Rewrite the integral using the factorization: \( \int \frac{dx}{x(x + 25)} \). This suggests using partial fraction decomposition to simplify the integrand.
Set up the partial fractions: \( \frac{1}{x(x + 25)} = \frac{A}{x} + \frac{B}{x + 25} \). Multiply both sides by \( x(x + 25) \) to find \( A \) and \( B \).
Solve for \( A \) and \( B \) by substituting convenient values for \( x \) (such as \( x = 0 \) and \( x = -25 \)) or by equating coefficients.
Once you have \( A \) and \( B \), rewrite the integral as \( \int \left( \frac{A}{x} + \frac{B}{x + 25} \right) dx \) and integrate each term separately using the natural logarithm function.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Integration of Rational Functions
This involves integrating functions expressed as ratios of polynomials. Techniques such as partial fraction decomposition are often used to simplify the integrand into manageable terms that can be integrated directly.
Recommended video:
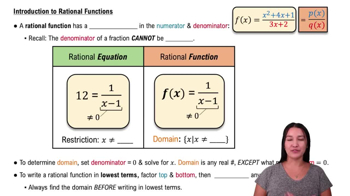
Intro to Rational Functions
Partial Fraction Decomposition
A method to break down complex rational expressions into simpler fractions. It is especially useful when the denominator factors into linear or quadratic terms, allowing easier integration of each component.
Recommended video:
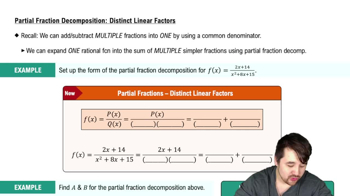
Partial Fraction Decomposition: Distinct Linear Factors
Algebraic Manipulation and Substitution
Rewriting expressions, such as recognizing that √(x² + 25x) = √x √(x + 25), helps simplify the integral. Substitution techniques can then be applied to transform the integral into a standard form for easier evaluation.
Recommended video:

Substitution With an Extra Variable

 8:38m
8:38mWatch next
Master Indefinite Integrals with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
17
views
