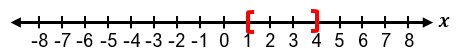
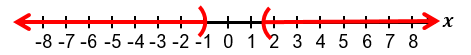
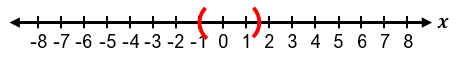
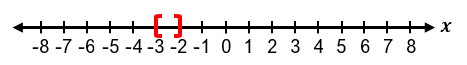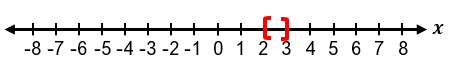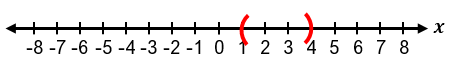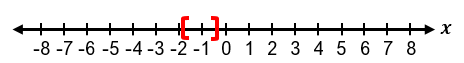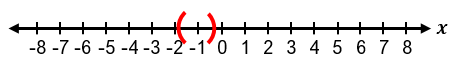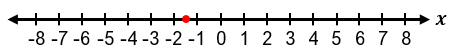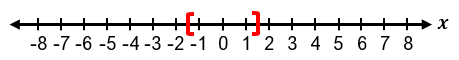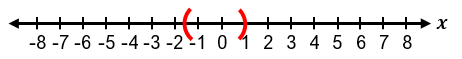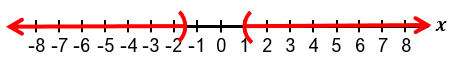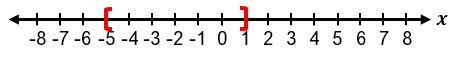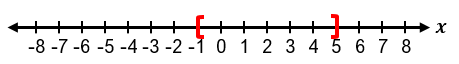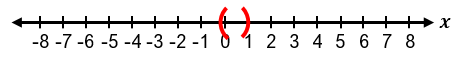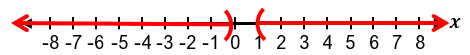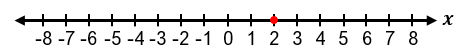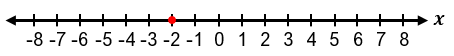Solving absolute value inequalities involves combining the techniques used for absolute value equations and inequalities. When faced with an inequality such as |x| < a, it means the distance between x and zero is less than a. This can be rewritten as a compound inequality: −a < x < a. Similarly, if the inequality is |x| ≤ a, it translates to −a ≤ x ≤ a. These forms allow us to solve the inequality by isolating the variable within a three-part inequality.
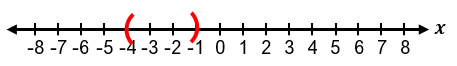
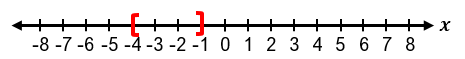
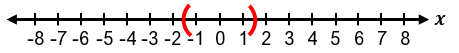
To solve absolute value inequalities, the first step is to isolate the absolute value expression on one side. For example, in an inequality like |x + 1| + 3 ≤ 5, subtracting 3 from both sides isolates the absolute value, resulting in |x + 1| ≤ 2. This can then be rewritten as the three-part inequality −2 ≤ x + 1 ≤ 2. Solving this involves subtracting 1 from all parts, yielding −3 ≤ x ≤ 1. The solution can be expressed in interval notation as [−3, 1], where brackets indicate that the endpoints are included due to the "less than or equal to" condition. Graphically, this solution is represented by a line segment between −3 and 1 with closed circles at both ends.
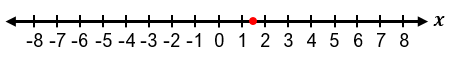
It is important to recognize special cases when dealing with absolute value inequalities. Since absolute value represents distance, it cannot be negative. Therefore, if the inequality is of the form |x| < negative number, it has no solution because the absolute value cannot be less than a negative number. If the inequality is |x| ≤ 0, the only solution is when the expression inside the absolute value equals zero, meaning x = 0. For example, if |x + 1| ≤ 0, then x + 1 = 0, so x = −1.
In summary, solving absolute value inequalities with "less than" or "less than or equal to" signs involves isolating the absolute value, rewriting the inequality as a three-part compound inequality, and solving for the variable. Special attention must be given to cases where the boundary value is zero or negative, as these determine whether solutions exist or are unique. Mastery of these steps enables effective solving and interpretation of absolute value inequalities in various mathematical contexts.