Compare the control of gene regulation in eukaryotes and bacteria at the level of initiation of transcription. How do the regulatory mechanisms work? What are the similarities and differences in these two types of organisms in terms of the specific components of the regulatory mechanisms?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
10. Transcription
Transcription in Eukaryotes
Problem 15
Textbook Question
Many promoter regions contain CAAT boxes containing consensus sequences CAAT or CCAAT approximately 70 to 80 bases upstream from the transcription start site. How might one determine the influence of CAAT boxes on the transcription rate of a given gene?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the gene of interest and locate its promoter region, specifically the CAAT box sequence approximately 70 to 80 bases upstream of the transcription start site.
Design an experiment to compare transcription rates by creating two versions of the gene's promoter: one with the intact CAAT box and one with a mutated or deleted CAAT box sequence.
Use a reporter gene assay by cloning each promoter variant upstream of a reporter gene (such as luciferase or GFP) to quantitatively measure transcriptional activity.
Transfect or transform appropriate cells with the constructs containing either the wild-type or mutated promoter and allow time for expression.
Measure and compare the reporter gene expression levels from both constructs; differences in expression will indicate the influence of the CAAT box on transcription rate.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Promoter Regions and Transcription Start Site
Promoter regions are DNA sequences located upstream of a gene that regulate transcription initiation. The transcription start site (TSS) is where RNA polymerase begins synthesizing RNA. Elements like CAAT boxes, found about 70-80 bases upstream, serve as binding sites for transcription factors that influence gene expression.
Recommended video:
Guided course
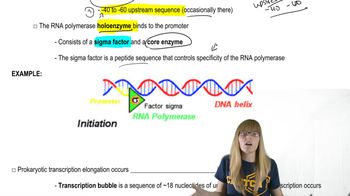
Prokaryotic Transcription
CAAT Box Function and Consensus Sequence
The CAAT box is a conserved DNA sequence (CAAT or CCAAT) within promoters that binds specific transcription factors to enhance or regulate transcription efficiency. Its presence can increase the rate of transcription by facilitating the assembly of the transcriptional machinery.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Sequencing Overview
Experimental Approaches to Assess Transcriptional Influence
To determine the effect of CAAT boxes on transcription rate, techniques like reporter gene assays, site-directed mutagenesis, or electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSAs) are used. These methods allow comparison of transcription levels with and without functional CAAT boxes, revealing their regulatory role.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Eukaryotic Transcription

 9:16m
9:16mWatch next
Master Eukaryotic Transcription with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
843
views
