Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses
Bacteriophage Genetics
Struggling with Genetics?
Join thousands of students who trust us to help them ace their exams!Watch the first videoMultiple Choice
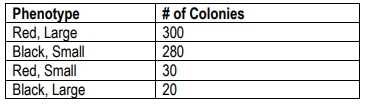
A mixed infection of two bacteriophage strains was performed. Infection of bacteriophage strain 1 causes the bacteria to be red and large, while infection of bacteriophage strain 2 causes the bacteria colony to be black and small. The following results were obtained. Using this data, determine the distance between the color and size genes.
A
45.3 m.u
B
15.7 m.u
C
7.9 m.u
D
2.2 m.u
0 Comments
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the parental and recombinant phenotypes. The parental phenotypes are Red, Large and Black, Small, as they are the most frequent. The recombinant phenotypes are Red, Small and Black, Large, as they are less frequent.
Calculate the total number of colonies by adding all the colonies: 300 (Red, Large) + 280 (Black, Small) + 30 (Red, Small) + 20 (Black, Large).
Determine the number of recombinant colonies by adding the numbers of the recombinant phenotypes: 30 (Red, Small) + 20 (Black, Large).
Calculate the recombination frequency by dividing the number of recombinant colonies by the total number of colonies, then multiply by 100 to convert it to a percentage.
The recombination frequency, expressed as a percentage, is equivalent to the map units (m.u) between the genes. This value will help you determine the genetic distance between the color and size genes.

 3:44m
3:44mWatch next
Master Plaques and Experiments with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Multiple Choice
In bacteriophages, which structure directly protects the viral DNA from degradation and environmental damage outside the host cell?
16
views
Bacteriophage Genetics practice set


