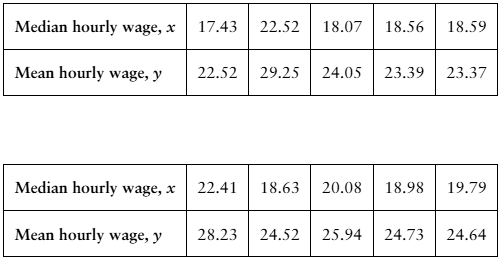
[DATA] The following data represent the height (inches) of boys between the ages of 2 and 10 years.
b. Compute the standard error of the estimate, Sₑ.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 7:38m
7:38mMaster Residuals and Residual Plots with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning