A frequency distribution lists the _____of occurrences of each category of data, while a relative frequency distribution lists the______of occurrences of each category of data.
Table of contents
- 1. Intro to Stats and Collecting Data1h 14m
- 2. Describing Data with Tables and Graphs1h 55m
- 3. Describing Data Numerically2h 5m
- 4. Probability2h 16m
- 5. Binomial Distribution & Discrete Random Variables3h 6m
- 6. Normal Distribution and Continuous Random Variables2h 11m
- 7. Sampling Distributions & Confidence Intervals: Mean3h 23m
- Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean and Central Limit Theorem19m
- Distribution of Sample Mean - Excel23m
- Introduction to Confidence Intervals15m
- Confidence Intervals for Population Mean1h 18m
- Determining the Minimum Sample Size Required12m
- Finding Probabilities and T Critical Values - Excel28m
- Confidence Intervals for Population Means - Excel25m
- 8. Sampling Distributions & Confidence Intervals: Proportion2h 10m
- 9. Hypothesis Testing for One Sample5h 8m
- Steps in Hypothesis Testing1h 6m
- Performing Hypothesis Tests: Means1h 4m
- Hypothesis Testing: Means - Excel42m
- Performing Hypothesis Tests: Proportions37m
- Hypothesis Testing: Proportions - Excel27m
- Performing Hypothesis Tests: Variance12m
- Critical Values and Rejection Regions28m
- Link Between Confidence Intervals and Hypothesis Testing12m
- Type I & Type II Errors16m
- 10. Hypothesis Testing for Two Samples5h 37m
- Two Proportions1h 13m
- Two Proportions Hypothesis Test - Excel28m
- Two Means - Unknown, Unequal Variance1h 3m
- Two Means - Unknown Variances Hypothesis Test - Excel12m
- Two Means - Unknown, Equal Variance15m
- Two Means - Unknown, Equal Variances Hypothesis Test - Excel9m
- Two Means - Known Variance12m
- Two Means - Sigma Known Hypothesis Test - Excel21m
- Two Means - Matched Pairs (Dependent Samples)42m
- Matched Pairs Hypothesis Test - Excel12m
- Two Variances and F Distribution29m
- Two Variances - Graphing Calculator16m
- 11. Correlation1h 24m
- 12. Regression3h 33m
- Linear Regression & Least Squares Method26m
- Residuals12m
- Coefficient of Determination12m
- Regression Line Equation and Coefficient of Determination - Excel8m
- Finding Residuals and Creating Residual Plots - Excel11m
- Inferences for Slope31m
- Enabling Data Analysis Toolpak1m
- Regression Readout of the Data Analysis Toolpak - Excel21m
- Prediction Intervals13m
- Prediction Intervals - Excel19m
- Multiple Regression - Excel29m
- Quadratic Regression15m
- Quadratic Regression - Excel10m
- 13. Chi-Square Tests & Goodness of Fit2h 21m
- 14. ANOVA2h 28m
2. Describing Data with Tables and Graphs
Frequency Distributions
Problem 2.2.27g
Textbook Question
Gini Index The Gini Index is a measure of how evenly income is distributed within a country, ranging from 0 to 100. An index of 0 suggests income is distributed with perfect equality. The higher the number, the worse the income inequality. The data below represent the Gini Index for a random sample of countries. Note: The United States has a Gini Index of 45 and Sweden has the lowest Gini Index. With a first class having a lower class limit of 20 and a class width of 5:
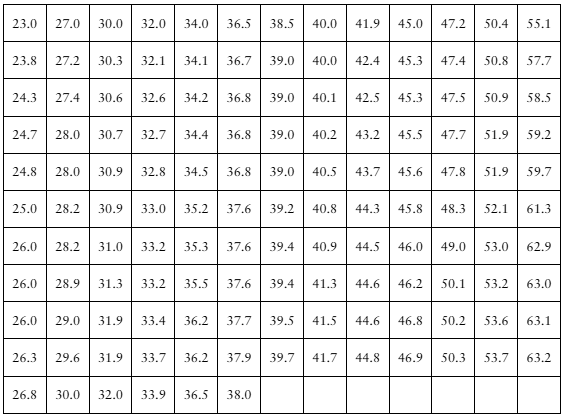
g. Does one frequency distribution provide a better summary of the data than the other? Explain.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the two frequency distributions being compared. One distribution uses class intervals starting at 20 with a class width of 5 (e.g., 20-24.9, 25-29.9, etc.), while the other distribution likely uses different class intervals or grouping methods. Identify the exact class intervals and frequencies for both distributions.
Step 2: Calculate the frequency for each class interval in both distributions by counting how many Gini Index values fall within each class. This will give you the frequency distribution tables for both methods.
Step 3: Analyze the shape and spread of each frequency distribution. Look for how well each distribution summarizes the data, considering factors such as the number of classes, the clarity of the distribution shape (e.g., skewness, modality), and how well the classes capture the variation in the data.
Step 4: Evaluate which frequency distribution provides a better summary by considering the balance between detail and simplicity. A better summary will have classes that are neither too broad (losing detail) nor too narrow (too many classes, making it complex), and it should clearly show the distribution pattern of the Gini Index values.
Step 5: Conclude by explaining which frequency distribution is more effective based on your analysis, supporting your reasoning with observations about the clarity, interpretability, and usefulness of the frequency tables in representing the income inequality data.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
5mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Frequency Distribution
A frequency distribution organizes data into classes or intervals, showing how many data points fall into each class. It helps summarize large data sets by grouping values, making patterns like skewness or concentration easier to identify. Choosing appropriate class widths and limits is crucial for an informative distribution.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Intro to Frequency Distributions
Gini Index
The Gini Index measures income inequality within a population, ranging from 0 (perfect equality) to 100 (maximum inequality). It provides a single value summarizing how income is distributed, useful for comparing countries or regions. Understanding its scale and interpretation is key to analyzing income data.
Comparing Frequency Distributions
When comparing frequency distributions, consider how well each summarizes the data's shape, spread, and key features. A better summary captures important details without oversimplifying or overcomplicating. Evaluating class width, number of classes, and clarity helps determine which distribution is more effective.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Intro to Frequency Distributions

 6:38m
6:38mWatch next
Master Intro to Frequency Distributions with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
30
views
