a. Patti and John each played 100 games of Solitaire on their smartphones. Patti won 7 games and estimated her probability of winning Solitaire as 0.07. John won 6 games and estimated his probability as 0.06. Why do their estimates differ?
Table of contents
- 1. Intro to Stats and Collecting Data1h 14m
- 2. Describing Data with Tables and Graphs1h 55m
- 3. Describing Data Numerically2h 5m
- 4. Probability2h 16m
- 5. Binomial Distribution & Discrete Random Variables3h 6m
- 6. Normal Distribution and Continuous Random Variables2h 11m
- 7. Sampling Distributions & Confidence Intervals: Mean3h 23m
- Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean and Central Limit Theorem19m
- Distribution of Sample Mean - Excel23m
- Introduction to Confidence Intervals15m
- Confidence Intervals for Population Mean1h 18m
- Determining the Minimum Sample Size Required12m
- Finding Probabilities and T Critical Values - Excel28m
- Confidence Intervals for Population Means - Excel25m
- 8. Sampling Distributions & Confidence Intervals: Proportion2h 10m
- 9. Hypothesis Testing for One Sample5h 8m
- Steps in Hypothesis Testing1h 6m
- Performing Hypothesis Tests: Means1h 4m
- Hypothesis Testing: Means - Excel42m
- Performing Hypothesis Tests: Proportions37m
- Hypothesis Testing: Proportions - Excel27m
- Performing Hypothesis Tests: Variance12m
- Critical Values and Rejection Regions28m
- Link Between Confidence Intervals and Hypothesis Testing12m
- Type I & Type II Errors16m
- 10. Hypothesis Testing for Two Samples5h 37m
- Two Proportions1h 13m
- Two Proportions Hypothesis Test - Excel28m
- Two Means - Unknown, Unequal Variance1h 3m
- Two Means - Unknown Variances Hypothesis Test - Excel12m
- Two Means - Unknown, Equal Variance15m
- Two Means - Unknown, Equal Variances Hypothesis Test - Excel9m
- Two Means - Known Variance12m
- Two Means - Sigma Known Hypothesis Test - Excel21m
- Two Means - Matched Pairs (Dependent Samples)42m
- Matched Pairs Hypothesis Test - Excel12m
- Two Variances and F Distribution29m
- Two Variances - Graphing Calculator16m
- 11. Correlation1h 24m
- 12. Regression3h 33m
- Linear Regression & Least Squares Method26m
- Residuals12m
- Coefficient of Determination12m
- Regression Line Equation and Coefficient of Determination - Excel8m
- Finding Residuals and Creating Residual Plots - Excel11m
- Inferences for Slope31m
- Enabling Data Analysis Toolpak1m
- Regression Readout of the Data Analysis Toolpak - Excel21m
- Prediction Intervals13m
- Prediction Intervals - Excel19m
- Multiple Regression - Excel29m
- Quadratic Regression15m
- Quadratic Regression - Excel10m
- 13. Chi-Square Tests & Goodness of Fit2h 21m
- 14. ANOVA2h 28m
4. Probability
Basic Concepts of Probability
Problem 5.2.45g
Textbook Question
"Putting It Together: Red-Light Cameras
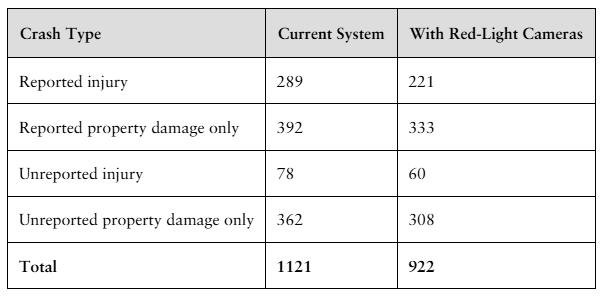
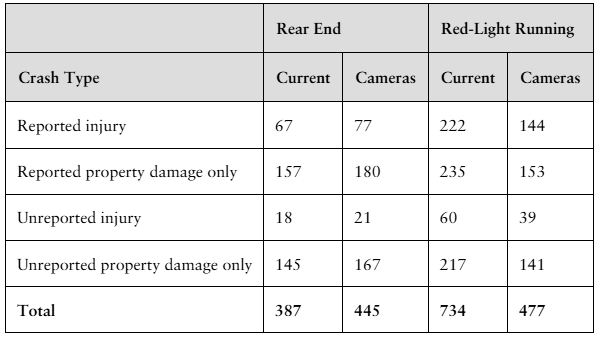
In a study of the feasibility of a red-light camera program in the city of Milwaukee, the data below summarize the projected number of crashes at 13 selected intersections over a five-year period.
(g) Based on the data shown, does it appear that the red-light camera program will be beneficial in reducing crashes at the intersections? Explain.
"
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the data provided. The first table shows the total number of crashes over five years at 13 intersections under the current system and with red-light cameras. The second table breaks down these crashes into two categories: Rear End and Red-Light Running, with counts for both the current system and with cameras.
Step 2: Compare the total number of crashes in the first table. Note the total crashes under the current system (1121) and with red-light cameras (922). This comparison gives an initial indication of whether the cameras reduce overall crashes.
Step 3: Analyze the breakdown in the second table. For Rear End crashes, compare the totals under the current system (387) and with cameras (445). For Red-Light Running crashes, compare the totals under the current system (734) and with cameras (477). This helps identify which type of crashes increase or decrease with the cameras.
Step 4: Consider the nature of the crashes. Red-Light Running crashes are generally more dangerous than Rear End crashes. Even if Rear End crashes increase, a reduction in Red-Light Running crashes might still indicate a safety benefit.
Step 5: Summarize your findings by weighing the reduction in total crashes and the changes in crash types. Use this to explain whether the red-light camera program appears beneficial in reducing crashes and improving safety at the intersections.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Comparative Data Analysis
Comparative data analysis involves examining two or more data sets to identify differences or trends. In this context, comparing crash numbers under the current system versus with red-light cameras helps determine if the intervention reduces crashes. Understanding how to interpret these differences is crucial for evaluating program effectiveness.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Collecting Data
Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics summarize and describe features of a data set, such as totals and category breakdowns. Here, totals of crashes and their types provide a clear overview of the situation before and after implementing red-light cameras, enabling straightforward comparison and insight into the program's impact.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Parameters vs. Statistics
Causation vs. Correlation
Distinguishing causation from correlation is essential when interpreting data. A reduction in crashes with red-light cameras suggests a correlation, but other factors might influence results. Understanding this helps avoid overestimating the program's effect without further controlled studies.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Correlation Coefficient

 5:37m
5:37mWatch next
Master Introduction to Probability with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
12
views
