The distribution of income tends to be skewed to the right. Suppose you are running for a congressional seat and wish to portray that the average income in your district is low. Which measure of central tendency, the mean or the median, would you report? Why?
Table of contents
- 1. Intro to Stats and Collecting Data1h 14m
- 2. Describing Data with Tables and Graphs1h 55m
- 3. Describing Data Numerically2h 5m
- 4. Probability2h 16m
- 5. Binomial Distribution & Discrete Random Variables3h 6m
- 6. Normal Distribution and Continuous Random Variables2h 11m
- 7. Sampling Distributions & Confidence Intervals: Mean3h 23m
- Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean and Central Limit Theorem19m
- Distribution of Sample Mean - Excel23m
- Introduction to Confidence Intervals15m
- Confidence Intervals for Population Mean1h 18m
- Determining the Minimum Sample Size Required12m
- Finding Probabilities and T Critical Values - Excel28m
- Confidence Intervals for Population Means - Excel25m
- 8. Sampling Distributions & Confidence Intervals: Proportion2h 10m
- 9. Hypothesis Testing for One Sample5h 8m
- Steps in Hypothesis Testing1h 6m
- Performing Hypothesis Tests: Means1h 4m
- Hypothesis Testing: Means - Excel42m
- Performing Hypothesis Tests: Proportions37m
- Hypothesis Testing: Proportions - Excel27m
- Performing Hypothesis Tests: Variance12m
- Critical Values and Rejection Regions28m
- Link Between Confidence Intervals and Hypothesis Testing12m
- Type I & Type II Errors16m
- 10. Hypothesis Testing for Two Samples5h 37m
- Two Proportions1h 13m
- Two Proportions Hypothesis Test - Excel28m
- Two Means - Unknown, Unequal Variance1h 3m
- Two Means - Unknown Variances Hypothesis Test - Excel12m
- Two Means - Unknown, Equal Variance15m
- Two Means - Unknown, Equal Variances Hypothesis Test - Excel9m
- Two Means - Known Variance12m
- Two Means - Sigma Known Hypothesis Test - Excel21m
- Two Means - Matched Pairs (Dependent Samples)42m
- Matched Pairs Hypothesis Test - Excel12m
- Two Variances and F Distribution29m
- Two Variances - Graphing Calculator16m
- 11. Correlation1h 24m
- 12. Regression3h 33m
- Linear Regression & Least Squares Method26m
- Residuals12m
- Coefficient of Determination12m
- Regression Line Equation and Coefficient of Determination - Excel8m
- Finding Residuals and Creating Residual Plots - Excel11m
- Inferences for Slope31m
- Enabling Data Analysis Toolpak1m
- Regression Readout of the Data Analysis Toolpak - Excel21m
- Prediction Intervals13m
- Prediction Intervals - Excel19m
- Multiple Regression - Excel29m
- Quadratic Regression15m
- Quadratic Regression - Excel10m
- 13. Chi-Square Tests & Goodness of Fit2h 21m
- 14. ANOVA2h 28m
3. Describing Data Numerically
Mode
Problem 3.1.29
Textbook Question
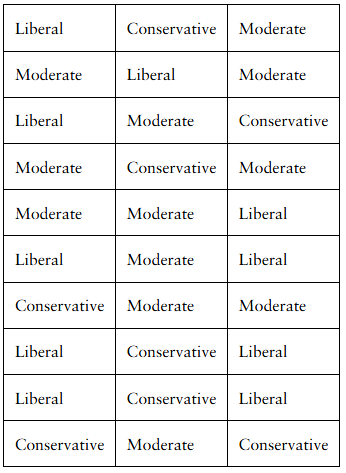
Political Views A sample of 30 registered voters was surveyed in which the respondents were asked, “Do you consider your political views to be conservative, moderate, or liberal?” The results of the survey are shown in the table.
a. Determine the mode political view.
b. Do you think it would be a good idea to rotate the choices conservative, moderate, or liberal in the question? Why?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Count the frequency of each political view (Liberal, Conservative, Moderate) from the sample of 30 responses. This means tally how many times each category appears in the table.
Step 2: Identify the mode by determining which political view has the highest frequency count. The mode is the category that appears most often in the data set.
Step 3: For part b, consider the concept of response bias in surveys. Think about whether the order of choices (Conservative, Moderate, Liberal) might influence how respondents answer, potentially causing bias.
Step 4: Reflect on the idea of rotating the order of choices to reduce any order bias. Explain why rotating the choices might help ensure that no particular option is favored simply because of its position in the list.
Step 5: Summarize your reasoning by discussing how rotating choices can improve the reliability and validity of survey responses by minimizing the effect of question order on respondents' answers.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Mode
The mode is the value that appears most frequently in a data set. In categorical data like political views, the mode identifies the most common category among respondents. It helps summarize the data by highlighting the most typical response.
Recommended video:

Mode
Frequency Distribution
Frequency distribution is a summary of how often each category or value occurs in a data set. Counting the number of times each political view appears allows us to organize and analyze the data effectively, which is essential for determining the mode.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Intro to Frequency Distributions
Survey Question Design and Response Bias
The order of response choices in a survey can influence how respondents answer, known as response bias. Rotating choices (randomizing order) helps reduce this bias, ensuring more accurate and reliable data by preventing respondents from favoring options based on their position.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Contingency Tables
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
37
views


