Can the Lyon hypothesis be tested in a human female who is homozygous for one allele of the X-linked G6PD gene? Why, or why not?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
6. Chromosomal Variation
Chromosomal Mutations: Aneuploidy
Problem 26
Textbook Question
In a recent cytogenetic study on 1021 cases of Down syndrome, 46 were the result of translocations, the most frequent of which was symbolized as t(14;21). What does this symbol represent, and how many chromosomes would you expect to be present in t(14;21) Down syndrome individuals?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand that the symbol t(14;21) represents a chromosomal translocation between chromosome 14 and chromosome 21. This means a segment of chromosome 21 is abnormally attached to chromosome 14, or vice versa.
Recall that in Down syndrome caused by translocation, the extra genetic material from chromosome 21 is present due to this rearrangement, rather than having a full extra chromosome 21 as in trisomy 21.
Recognize that a normal human karyotype has 46 chromosomes, arranged in 23 pairs. In translocation Down syndrome, the total chromosome number can be different depending on whether the translocation is balanced or unbalanced.
Determine that in the common t(14;21) translocation causing Down syndrome, the individual typically has 45 chromosomes because two chromosomes have fused into one (the translocation chromosome), but there is still an extra copy of the critical part of chromosome 21.
Summarize that the t(14;21) symbol indicates a translocation between chromosomes 14 and 21, and individuals with this translocation Down syndrome usually have 45 chromosomes instead of the typical 46.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Chromosomal Translocations
A chromosomal translocation occurs when a segment from one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome. In Down syndrome, a common translocation involves chromosomes 14 and 21, denoted as t(14;21), where part of chromosome 21 is translocated to chromosome 14. This can lead to an extra copy of chromosome 21 material, causing the syndrome.
Recommended video:
Guided course
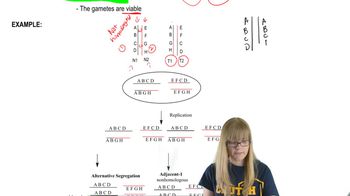
Reciprocal Translocation
Karyotype and Chromosome Number
A normal human karyotype has 46 chromosomes arranged in 23 pairs. In translocation Down syndrome, the total chromosome count can remain 46 because the extra chromosome 21 material is attached to another chromosome rather than existing as a separate chromosome. Thus, individuals with t(14;21) typically have 46 chromosomes, but with an abnormal structure.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Human Sex Chromosomes
Down Syndrome Genetic Mechanism
Down syndrome is caused by trisomy 21, meaning three copies of chromosome 21 material. In translocation cases like t(14;21), the extra chromosome 21 material is attached to chromosome 14, resulting in functional trisomy 21 despite a normal chromosome count. This explains the presence of Down syndrome traits without the typical 47 chromosomes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

History of Genetics
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
573
views


