Contrast the structure of SINE and LINE DNA sequences. Why are LINEs referred to as retrotransposons?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
16. Transposable Elements
Transposable Elements in Eukaryotes
Problem 23
Textbook Question
The human genome contains approximately 106 copies of an Alu sequence, one of the best-studied classes of short interspersed elements (SINEs), per haploid genome. Individual Alu units share a 282-nucleotide consensus sequence followed by a 3'-adenine-rich tail region [Schmid (1998)]. Given that there are approximately 3 x 109 base pairs per human haploid genome, about how many base pairs are spaced between each Alu sequence?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the total number of base pairs in the human haploid genome, which is given as approximately \$3 \times 10^{9}$ base pairs.
Note the total number of Alu sequences per haploid genome, which is approximately \$10^{6}$ copies.
Understand that the problem asks for the average spacing between each Alu sequence, meaning the average number of base pairs between consecutive Alu elements.
Calculate the average spacing by dividing the total number of base pairs by the total number of Alu sequences using the formula:
\(\text{Average spacing} = \frac{\text{Total base pairs}}{\text{Number of Alu sequences}}\)
Substitute the given values into the formula:
\(\text{Average spacing} = \frac{3 \times 10^{9}}{10^{6}}\)
This will give the average number of base pairs between each Alu sequence.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Human Genome Size and Structure
The human haploid genome contains about 3 billion base pairs (3 x 10^9 bp). This total DNA length is organized into chromosomes and includes coding and non-coding regions. Understanding genome size is essential for calculating average distances between repeated sequences like Alu elements.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Human Genome Composition
Alu Sequences and Short Interspersed Elements (SINEs)
Alu sequences are a type of SINE, approximately 282 base pairs long, repeated about one million times per haploid genome. These repetitive elements are dispersed throughout the genome and can be used as markers for genetic studies. Their abundance affects genome structure and spacing calculations.
Recommended video:
Guided course
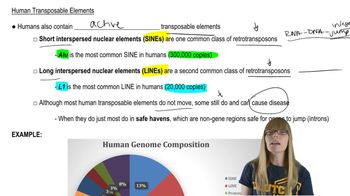
Human Transposable Elements
Calculating Average Spacing Between Repetitive Elements
To find the average spacing between repetitive sequences, divide the total genome size by the number of repeats. This gives the average number of base pairs between each element, assuming even distribution. This concept helps estimate genomic distances between Alu sequences.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Discovery

 3:14m
3:14mWatch next
Master Eukaryotic Transposable Elements with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1062
views
