
During oogenesis in an animal species with a haploid number of 6, one dyad undergoes nondisjunction during meiosis II. Following the second meiotic division, this dyad ends up intact in the ovum. How many chromosomes are present in
(a) the mature ovum and
(b) the second polar body?
(c) Following fertilization by a normal sperm, what chromosome condition is created?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
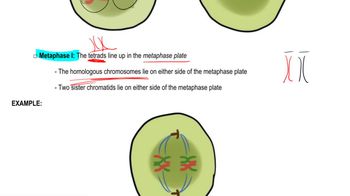
Key Concepts
Meiosis and Chromosome Number

Nondisjunction During Meiosis II
Fertilization and Aneuploidy

A diploid cell contains three pairs of homologous chromosomes designated C1 and C2, M1 and M2, and S1 and S2. No crossing over occurs. What combinations of chromosomes are possible in?
(a) daughter cells following mitosis
(b) cells undergoing the first meiotic metaphase
(c) haploid cells following both divisions of meiosis
Considering Problem 15, predict the number of different haploid cells that could be produced by meiosis if a fourth chromosome pair (W1 and W2) were added.
What is the probability that, in an organism with a haploid number of 10, a sperm will be formed that contains all 10 chromosomes whose centromeres were derived from maternal homologs?
The nuclear DNA content of a single sperm cell in Drosophila melanogaster is approximately 0.18 picogram. What would be the expected nuclear DNA content of a primary spermatocyte in Drosophila? What would be the expected nuclear DNA content of a somatic cell (non-sex cell) in the G1 phase? What would be the expected nuclear DNA content of a somatic cell at metaphase?
Contrast the chromatin fiber with the mitotic chromosome. How are the two structures related?
