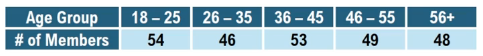
In Exercises 5–20, conduct the hypothesis test and provide the test statistic and the P-value and/or critical value, and state the conclusion.
Testing a Slot Machine The author purchased a slot machine (Bally Model 809) and tested it by playing it 1197 times. There are 10 different categories of outcomes, including no win, win jackpot, win with three bells, and so on. When testing the claim that the observed outcomes agree with the expected frequencies, the author obtained a test statistic of x2 = 8.815 Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that the actual outcomes agree with the expected frequencies. Does the slot machine appear to be functioning as expected?