Which of the following sequences correctly represents the flow of electrons during photosynthesis?
a. NADPH → O2 → CO2
b. H2O → NADPH → Calvin cycle
c. H2O → photosystem I → photosystem II
d. NADPH → electron transport chain → O2

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

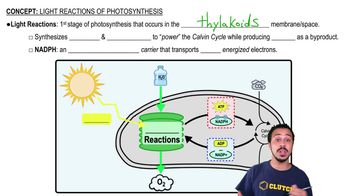

Which of the following sequences correctly represents the flow of electrons during photosynthesis?
a. NADPH → O2 → CO2
b. H2O → NADPH → Calvin cycle
c. H2O → photosystem I → photosystem II
d. NADPH → electron transport chain → O2
How is photosynthesis similar in C4 plants and CAM plants?
a. In both cases, only photosystem I is used.
b. Both types of plants make sugar without the Calvin cycle.
c. In both cases, rubisco is not used to fix carbon initially.
d. Both types of plants make most of their sugar in the dark.
Which of the following statements is a correct distinction between autotrophs and heterotrophs?
a. Autotrophs, but not heterotrophs, can nourish themselves beginning with CO2 and other nutrients that are inorganic.
b. Only heterotrophs require chemical compounds from the environment.
c. Cellular respiration is unique to heterotrophs.
d. Only heterotrophs have mitochondria.