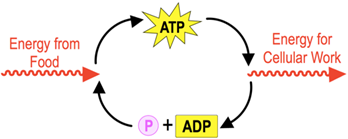
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a crucial high-energy molecule that powers various cellular activities. The structure of ATP consists of three primary components: a pentose sugar, an adenine nitrogenous base, and a chain of three phosphate groups. The term "triphosphate" indicates the presence of these three phosphate groups, which are essential for ATP's energy-storing capabilities.
When a cell has a high concentration of ATP, it possesses ample energy, while a low concentration indicates limited energy availability. The energy stored in ATP is released through a process known as ATP hydrolysis. This process involves breaking the bonds between the phosphate groups, which generates chemical energy that the cell can utilize. During hydrolysis, ATP is converted into adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and a free phosphate group. The "di" in ADP signifies that it contains two phosphate groups, as opposed to the three found in ATP.
In some cases, ADP can undergo further hydrolysis to form adenosine monophosphate (AMP), which contains only one phosphate group. The hydrolysis of ATP and ADP is facilitated by the addition of water, a process where the water molecule helps break the bonds between the phosphate groups. This reaction not only releases energy but also allows the released phosphate group to be utilized in other biochemical reactions.
Overall, ATP serves as the primary energy currency of the cell, and understanding its structure and function is fundamental to grasping how energy is transferred and utilized in biological systems. As we continue to explore ATP, we will delve deeper into its role in various cellular processes and the mechanisms by which energy is harnessed and expended.



 1 student found this helpful
1 student found this helpful