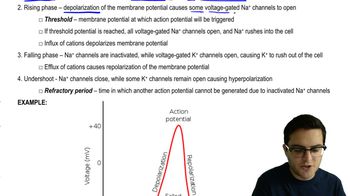
A common feature of action potentials is that they
a. Cause the membrane to hyperpolarize and then depolarize
b. Can undergo temporal and spatial summation
c. Are triggered by a depolarization that reaches threshold
d. Move at the same speed along all axons