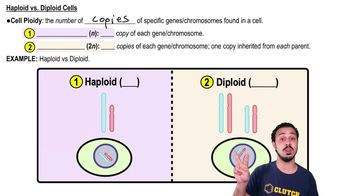
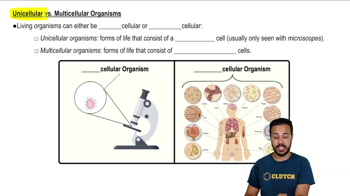
Biologists think that endosymbiosis gave rise to mitochondria before plastids partly because
a. The products of photosynthesis could not be metabolized without mitochondrial enzymes.
b. All eukaryotes have mitochondria (or their remnants), whereas many eukaryotes do not have plastids.
c. Mitochondrial DNA is less similar to prokaryotic DNA than is plastid DNA.
d. Without mitochondrial CO2 production, photosynthesis could not occur.