12. Microbial Metabolism
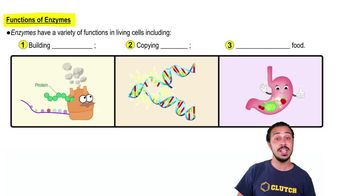
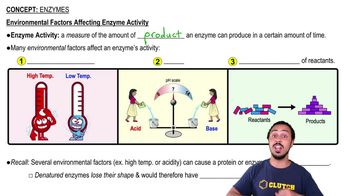
Enzymes
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following are examples of the functions of enzymes?
a) A lactase enzyme breaking down lactose sugar in the small intestine.
b) A DNA polymerase enzyme synthesizing new strands of DNA.
c) A lipase enzyme breaking down fats (lipids) in the small intestine.
d) A helicase enzyme unraveling DNA so it can be replicated.
e) All of the above.
5634views46rank - Multiple Choice
Which characteristics are likely associated with an enzyme isolated from a human stomach where conditions are strongly acidic.
a) An enzyme that functions properly at 70 degrees Fahrenheit and at a neutral pH.
b) An enzyme that functions properly at 98 degrees Fahrenheit and at an acidic pH.
c) An enzyme that functions properly at 98 degrees Fahrenheit and at a neutral pH.
d) An enzyme that functions properly at 70 degrees Fahrenheit and at an acidic pH.
4848views46rank - Textbook Question
Bacteria use the enzyme urease to obtain nitrogen in a form they can use from urea in the following reaction:
What purpose does the enzyme serve in this reaction? What type of reaction is this?
919views - Textbook Question
Define and explain the importance of each of the following:
a. Catalase
b. Hydrogen peroxide
c. Peroxidase
d. Superoxide radical
e. Superoxide dismutase
906views - Textbook Question
An organism that has peroxidase and superoxide dismutase but lacks catalase is most likely an
a. aerobe.
b. aerotolerant anaerobe.
c. obligate anaerobe.
1006views - Textbook Question
Suppose you inoculate three flasks of minimal salts broth with E. coli. Flask A contains glucose. Flask B contains glucose and lactose. Flask C contains lactose. After a few hours of incubation, you test the flasks for the presence of ß-galactosidase. Which flask(s) do you predict will have this enzyme?
a. A
b. B
c. C
d. A and B
e. B and C
904views