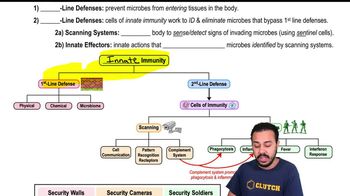
19. Innate Immunity
Introduction to Innate Immunity
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Skin and mucous membranes are mostly involved in:
1317views7rank - Multiple Choice
The 1st line of defense that the body uses to prevent infection includes?
1182views3rank - Multiple Choice
A patient consumed food contaminated with pathogenic bacteria. However, the patient did not become ill. The doctor explained to the patient that the acidity of the patient's stomach can kill many organisms, including bacteria. This type of protection would be classified as?
1109views6rank - Multiple Choice
Antibodies are a part of which type of immunity and why?
1131views6rank - Textbook Question
Are the following involved in innate or in adaptive immunity? Identify the role of each in immunity:
a. TLRs
b. transferrins
c. antimicrobial peptides
850views - Textbook Question
Which of the following is not a feature of innate immunity?
a. Better protection upon later exposure to a given pathogen
b. Recognition of diverse pathogens
c. Discrimination between self and foreign
d. Killing of identified invaders
e. Stimulation of adaptive immunity
976views - Textbook Question
Why is innate immunity considered a generalized defense?
1299views - Textbook Question
Write the letter of the description that applies to each of the following terms:
1. ___ Goblet cell
2. ___ Lysozyme
3. ___ Stem cell
4. ___ Dendritic cell
5. ___ Cell from sebaceous gland
6. ___ Bone marrow stem cell
7. ___ Eosinophil
8. ___ Alveolar macrophage
9. ___ Microglia
10. ___ Wandering macrophage
A. Leukocyte that primarily attacks parasitic worms
B. Phagocytic cell in lungs
C. Secretes sebum
D. Devours pathogens in epidermis
E. Breaks bonds in bacterial cell wall
F. Phagocytic cell in central nervous system
G. Generative cell with many types of offspring
H. Develops into formed elements of blood
I. Intercellular scavenger
J. Secretes mucus
757views