What do steroid and peptide hormones typically have in common?
a. Their solubility in cell membranes
b. Their requirement for travel through the bloodstream
c. The location of their receptors
d. Their reliance on signal transduction in the cell

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
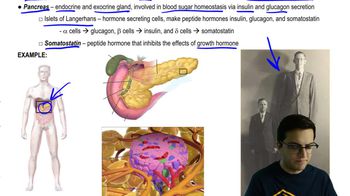

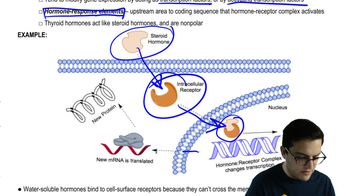
What do steroid and peptide hormones typically have in common?
a. Their solubility in cell membranes
b. Their requirement for travel through the bloodstream
c. The location of their receptors
d. Their reliance on signal transduction in the cell
Which of the following is the most likely explanation for hypothyroidism in a patient whose iodine level is normal?
a. Greater production of T3 than of T4
b. Hyposecretion of TSH
c. Hypersecretion of MSH
d. A decrease in the thyroid secretion of calcitonin
The relationship between the insect hormones ecdysteroid and PTTH is an example of
a. An interaction of the endocrine and nervous systems.
b. Homeostasis achieved by positive feedback.
c. Homeostasis maintained by antagonistic hormones.
d. Competitive inhibition of a hormone receptor.