Multiple Choice
Identify the element with the given electron orbital diagram.
4268
views
14
rank
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance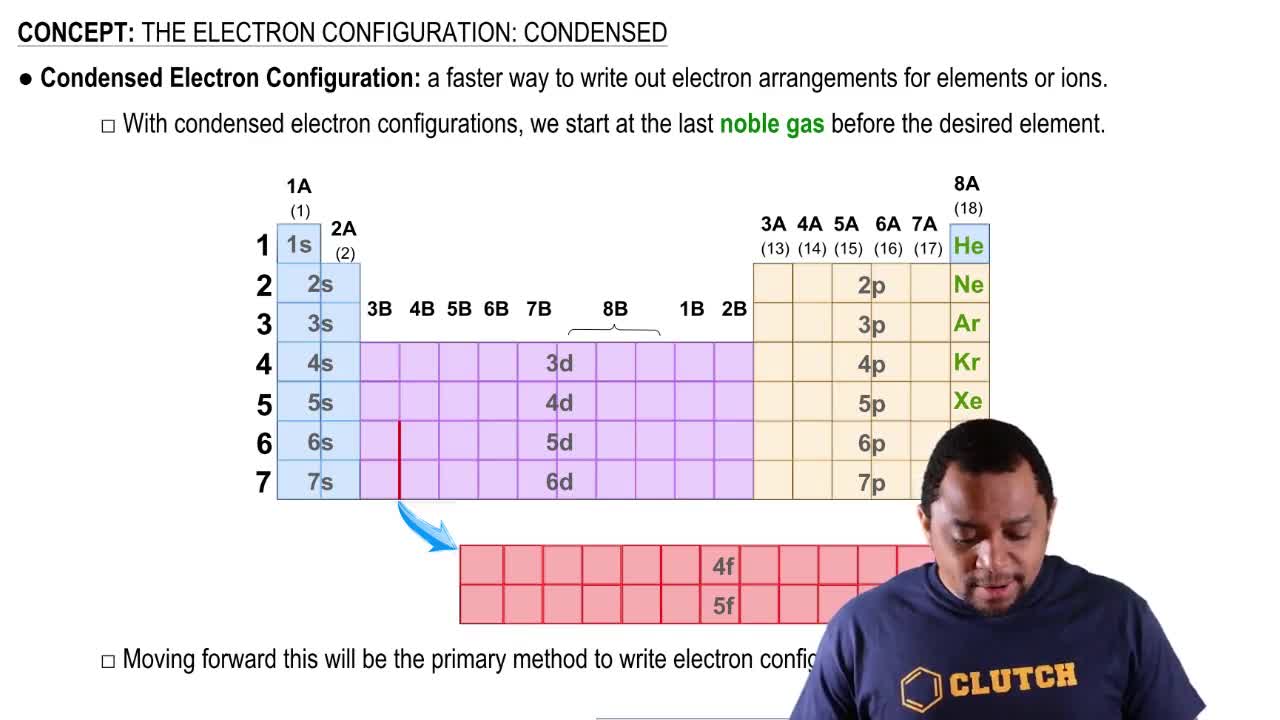



 2:15m
2:15mMaster The Electron Configuration (Simplified) Concept 1 with a bite sized video explanation from Jules
Start learning