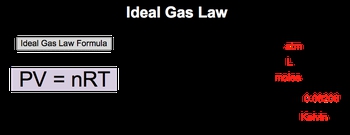
In the study of gas behavior, the ideal gas law serves as a fundamental equation that describes how gases respond to changes in pressure, volume, moles, and temperature. The ideal gas law is expressed by the formula:
\( PV = nRT \)
In this equation, \( P \) represents pressure, measured in atmospheres (atm), \( V \) denotes volume in liters (L), \( n \) is the number of moles of gas, \( R \) is the ideal gas constant, typically valued at \( 0.08206 \, \text{L} \cdot \text{atm} / (\text{K} \cdot \text{mol}) \), and \( T \) signifies temperature in Kelvins (K). Understanding this relationship is crucial, as it underpins various calculations and concepts related to gas behavior throughout the chapter.
To effectively utilize the ideal gas law, one must be familiar with the units associated with each variable, ensuring accurate application in problem-solving scenarios. Mastery of this formula will be essential for tackling a range of questions and practical applications in the study of gases.