Define and draw a motor unit.
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology5h 43m
- What is Anatomy & Physiology?22m
- Levels of Organization13m
- Variation in Anatomy & Physiology12m
- Introduction to Organ Systems27m
- Homeostasis10m
- Feedback Loops11m
- Feedback Loops: Negative Feedback19m
- Feedback Loops: Positive Feedback11m
- Anatomical Position7m
- Introduction to Directional Terms3m
- Directional Terms: Up and Down9m
- Directional Terms: Front and Back6m
- Directional Terms: Body Sides12m
- Directional Terms: Limbs6m
- Directional Terms: Depth Within the Body4m
- Introduction to Anatomical Terms for Body Regions3m
- Anatomical Terms for the Head and Neck8m
- Anatomical Terms for the Front of the Trunk8m
- Anatomical Terms for the Back9m
- Anatomical Terms for the Arm and Hand9m
- Anatomical Terms for the Leg and Foot15m
- Review- Using Anatomical Terms and Directions12m
- Abdominopelvic Quadrants and Regions19m
- Anatomical Planes & Sections17m
- Organization of the Body: Body Cavities13m
- Organization of the Body: Serous Membranes14m
- Organization of the Body: Serous Membrane Locations8m
- Organization of the Body: Thoracic Cavity8m
- Organization of the Body: Abdominopelvic Cavity12m
- 2. Cell Chemistry & Cell Components12h 39m
- Atoms- Smallest Unit of Matter57m
- Isotopes39m
- Introduction to Chemical Bonding19m
- Covalent Bonds40m
- Noncovalent Bonds5m
- Ionic Bonding37m
- Hydrogen Bonding19m
- Introduction to Water7m
- Properties of Water- Cohesion and Adhesion7m
- Properties of Water- Density8m
- Properties of Water- Thermal14m
- Properties of Water- The Universal Solvent17m
- Acids and Bases12m
- pH Scale21m
- Carbon8m
- Functional Groups9m
- Introduction to Biomolecules2m
- Monomers & Polymers11m
- Carbohydrates23m
- Proteins28m
- Nucleic Acids34m
- Lipids28m
- Microscopes11m
- Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells26m
- Introduction to Eukaryotic Organelles14m
- Endomembrane System: Protein Secretion30m
- Endomembrane System: Digestive Organelles14m
- Mitochondria & Chloroplasts21m
- Endosymbiotic Theory10m
- Introduction to the Cytoskeleton11m
- Cell Junctions8m
- Biological Membranes11m
- Types of Membrane Proteins8m
- Concentration Gradients and Diffusion9m
- Introduction to Membrane Transport16m
- Passive vs. Active Transport14m
- Osmosis30m
- Simple and Facilitated Diffusion17m
- Active Transport30m
- Endocytosis and Exocytosis15m
- 3. Energy & Cell Processes10h 8m
- Introduction to Energy15m
- Laws of Thermodynamics15m
- Chemical Reactions9m
- ATP22m
- Enzymes14m
- Enzyme Activation Energy9m
- Enzyme Binding Factors9m
- Enzyme Inhibition10m
- Introduction to Metabolism8m
- Redox Reactions15m
- Introduction to Cellular Respiration22m
- Types of Phosphorylation14m
- Glycolysis19m
- Pyruvate Oxidation8m
- Krebs Cycle16m
- Electron Transport Chain10m
- Chemiosmosis7m
- Review of Aerobic Cellular Respiration19m
- Fermentation & Anaerobic Respiration23m
- Introduction to Cell Division22m
- Organization of DNA in the Cell17m
- Introduction to the Cell Cycle7m
- Interphase18m
- Phases of Mitosis48m
- Cytokinesis16m
- Cell Cycle Regulation18m
- Review of the Cell Cycle7m
- Cancer13m
- Introduction to DNA Replication22m
- DNA Repair8m
- Central Dogma7m
- Introduction to Transcription20m
- Steps of Transcription19m
- Genetic Code25m
- Introduction to Translation30m
- Steps of Translation23m
- Post-Translational Modification6m
- 4. Tissues & Histology10h 3m
- Introduction to Tissues & Histology16m
- Introduction to Epithelial Tissue24m
- Characteristics of Epithelial Tissue37m
- Structural Naming of Epithelial Tissue19m
- Simple Epithelial Tissues1h 2m
- Stratified Epithelial Tissues55m
- Identifying Types of Epithelial Tissue32m
- Glandular Epithelial Tissue26m
- Introduction to Connective Tissue36m
- Classes of Connective Tissue8m
- Introduction to Connective Tissue Proper40m
- Connective Tissue Proper: Loose Connective Tissue56m
- Connective Tissue Proper: Dense Connective Tissue49m
- Specialized Connective Tissue: Cartilage44m
- Specialized Connective Tissue: Bone12m
- Specialized Connective Tissue: Blood9m
- Introduction to Muscle Tissue7m
- Types of Muscle Tissue45m
- Introduction to Nervous Tissue8m
- Nervous Tissue: The Neuron8m
- 5. Integumentary System2h 28m
- 6. Bones & Skeletal Tissue2h 16m
- An Introduction to Bone and Skeletal Tissue18m
- Gross Anatomy of Bone: Compact and Spongy Bone7m
- Gross Anatomy of Bone: Periosteum and Endosteum11m
- Gross Anatomy of Bone: Bone Marrow8m
- Gross Anatomy of Bone: Short, Flat, and Irregular Bones5m
- Gross Anatomy of Bones - Structure of a Long Bone23m
- Microscopic Anatomy of Bones - Bone Matrix9m
- Microscopic Anatomy of Bones - Bone Cells25m
- Microscopic Anatomy of Bones - The Osteon17m
- Microscopic Anatomy of Bones - Trabeculae9m
- 7. The Skeletal System2h 35m
- 8. Joints2h 17m
- 9. Muscle Tissue2h 33m
- 10. Muscles1h 11m
- 11. Nervous Tissue and Nervous System1h 35m
- 12. The Central Nervous System1h 6m
- 13. The Peripheral Nervous System1h 26m
- Introduction to the Peripheral Nervous System5m
- Organization of Sensory Pathways16m
- Introduction to Sensory Receptors5m
- Sensory Receptor Classification by Modality6m
- Sensory Receptor Classification by Location8m
- Proprioceptors7m
- Adaptation of Sensory Receptors8m
- Introduction to Reflex Arcs13m
- Reflex Arcs15m
- 14. The Autonomic Nervous System1h 38m
- 15. The Special Senses2h 41m
- 16. The Endocrine System2h 47m
- 17. The Blood3h 22m
- 18. The Heart3h 42m
- 19. The Blood Vessels3h 35m
- 20. The Lymphatic System3h 16m
- 21. The Immune System14h 37m
- Introduction to the Immune System10m
- Introduction to Innate Immunity17m
- Introduction to First-Line Defenses5m
- Physical Barriers in First-Line Defenses: Skin13m
- Physical Barriers in First-Line Defenses: Mucous Membrane9m
- First-Line Defenses: Chemical Barriers24m
- First-Line Defenses: Normal Microbiota7m
- Introduction to Cells of the Immune System15m
- Cells of the Immune System: Granulocytes28m
- Cells of the Immune System: Agranulocytes26m
- Introduction to Cell Communication5m
- Cell Communication: Surface Receptors & Adhesion Molecules16m
- Cell Communication: Cytokines27m
- Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs)48m
- Introduction to the Complement System24m
- Activation Pathways of the Complement System23m
- Effects of the Complement System23m
- Review of the Complement System13m
- Phagocytosis17m
- Introduction to Inflammation18m
- Steps of the Inflammatory Response28m
- Fever8m
- Interferon Response25m
- Review Map of Innate Immunity
- Introduction to Adaptive Immunity32m
- Antigens12m
- Introduction to T Lymphocytes38m
- Major Histocompatibility Complex Molecules20m
- Activation of T Lymphocytes21m
- Functions of T Lymphocytes25m
- Review of Cytotoxic vs Helper T Cells13m
- Introduction to B Lymphocytes27m
- Antibodies14m
- Classes of Antibodies35m
- Outcomes of Antibody Binding to Antigen15m
- T Dependent & T Independent Antigens21m
- Clonal Selection20m
- Antibody Class Switching17m
- Affinity Maturation14m
- Primary and Secondary Response of Adaptive Immunity21m
- Immune Tolerance28m
- Regulatory T Cells10m
- Natural Killer Cells16m
- Review of Adaptive Immunity25m
- 22. The Respiratory System3h 20m
- 23. The Digestive System3h 5m
- 24. Metabolism and Nutrition4h 0m
- Essential Amino Acids5m
- Lipid Vitamins19m
- Cellular Respiration: Redox Reactions15m
- Introduction to Cellular Respiration22m
- Cellular Respiration: Types of Phosphorylation14m
- Cellular Respiration: Glycolysis19m
- Cellular Respiration: Pyruvate Oxidation8m
- Cellular Respiration: Krebs Cycle16m
- Cellular Respiration: Electron Transport Chain14m
- Cellular Respiration: Chemiosmosis7m
- Review of Aerobic Cellular Respiration18m
- Fermentation & Anaerobic Respiration23m
- Gluconeogenesis16m
- Fatty Acid Oxidation20m
- Amino Acid Oxidation17m
- 25. The Urinary System2h 39m
- 26. Fluid and Electrolyte Balance, Acid Base Balance37m
- 27. The Reproductive System2h 5m
- 28. Human Development1h 21m
- 29. Heredity3h 32m
9. Muscle Tissue
Steps of Muscle Contraction
Problem 5
Textbook Question
What is the basic mechanism of contraction at the level of myofilaments?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand that muscle contraction occurs at the level of the sarcomere, the functional unit of a muscle fiber, which contains thick filaments (myosin) and thin filaments (actin). The interaction between these filaments is responsible for contraction.
Learn about the sliding filament theory, which explains that contraction occurs when the thin filaments (actin) slide past the thick filaments (myosin), shortening the sarcomere without changing the length of the filaments themselves.
Recognize the role of calcium ions (Ca²⁺) in initiating contraction. When a muscle is stimulated, Ca²⁺ is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and binds to troponin, a regulatory protein on the thin filament. This causes a conformational change in tropomyosin, exposing the myosin-binding sites on actin.
Understand the cross-bridge cycle: Myosin heads, which are energized by ATP hydrolysis, bind to the exposed sites on actin, forming cross-bridges. The myosin heads then pivot (power stroke), pulling the actin filaments toward the center of the sarcomere. ATP is required to detach the myosin heads and reset them for another cycle.
Recognize that contraction continues as long as Ca²⁺ levels remain elevated and ATP is available. When stimulation ceases, Ca²⁺ is actively pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, tropomyosin re-covers the binding sites on actin, and the muscle relaxes.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Play a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Myofilaments
Myofilaments are the contractile proteins found within muscle fibers, primarily composed of actin (thin filaments) and myosin (thick filaments). These proteins interact to facilitate muscle contraction through a process known as the sliding filament theory, where myosin heads attach to actin filaments and pull them inward, shortening the muscle fiber.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Intro to Muscle Tissue
Sliding Filament Theory
The sliding filament theory explains how muscle contraction occurs at the molecular level. According to this theory, during contraction, myosin heads bind to actin filaments, forming cross-bridges. The myosin heads then pivot, pulling the actin filaments toward the center of the sarcomere, which is the basic unit of muscle contraction, resulting in muscle shortening.
Recommended video:
Guided course
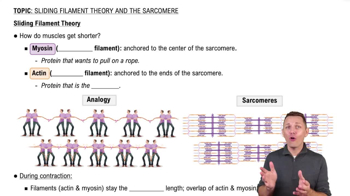
Sliding Filament Theory
Calcium Ions and ATP
Calcium ions (Ca2+) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) are crucial for muscle contraction. When a muscle is stimulated, calcium is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, enabling the binding of myosin to actin. ATP provides the energy required for the myosin heads to detach from actin and re-cock for another contraction cycle, ensuring continuous muscle activity.
Recommended video:
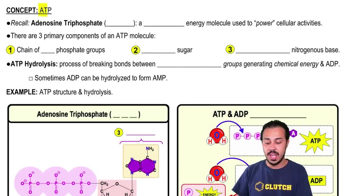
ATP

 4:53m
4:53mWatch next
Master Overview of Muscle Contraction with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1075
views
1
rank
