34. Wave Optics
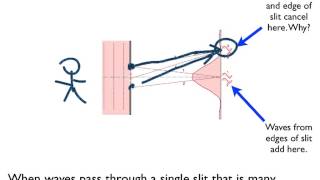
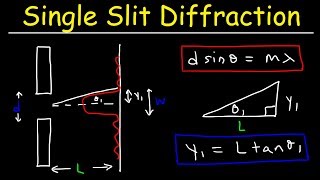
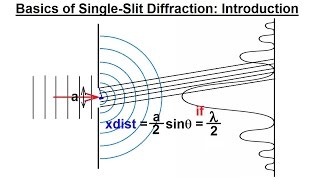
Single Slit Diffraction
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Light from a 600 nm laser is shown through a single slit of unknown width. If a screen is placed 4.5 m behind the slit captures a diffraction patter with a central bright fringe of width 20 mm, what is the width of the single slit?
977views17rank2comments - Multiple ChoiceA single slit is illuminated by coherent monochromatic light at On a screen behind the slit, a central bright spot is observed to have a width of What is the width of the single slit?1079views
- Multiple ChoiceA carbon dioxide laser produceselectromagnetic waves, which pass through a circular aperture with diameter What is the approximate width of the laser beam when it strikes a target away?1236views
- Multiple ChoiceA single slit is illuminated by coherent monochromatic light at . On a screen behind the slit, a central bright spot is observed to have a width of . What is the width of the single slit?812views
- Textbook Question
In a single-slit experiment, the slit width is 200 times the wavelength of the light. What is the width (in mm) of the central maximum on a screen 2.0 m behind the slit?
93views - Textbook Question
Light of 630 nm wavelength illuminates a single slit of width 0.15 mm. FIGURE EX33.22 shows the intensity pattern seen on a screen behind the slit. What is the distance to the screen?
109views - Textbook Question
Light of 600 nm wavelength passes through a single slit and creates a 2.0-cm-wide central maximum on a screen behind the slit. What wavelength of light will create a 3.0-cm-wide central maximum on a screen twice as far away?
63views - Textbook Question
Figure EX33.26 shows the light intensity on a screen behind a single slit. The wavelength of the light is 600 nm and the slit width is 0.15 mm. What is the distance from the slit to the screen?
62views