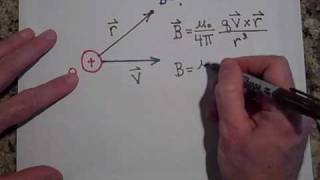
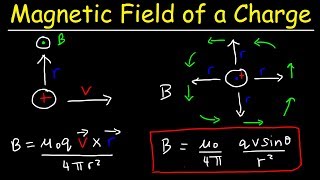
29. Sources of Magnetic Field
Magnetic Field Produced by Moving Charges
29. Sources of Magnetic Field
Magnetic Field Produced by Moving Charges
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceAs a proton passes the origin, its velocity is in the positive x direction. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field at the point (, , )?701views
- Multiple ChoiceAs a proton passes the origin, its velocity is in the positive x direction. What is the direction of the magnetic field at the point (, , )?559views
- Multiple ChoiceA charged particle moving in a magnetic field has a force to the top of the page when it is moving toward the right and the field is into the page. Is this particle positive, negative or neutral?835views
- Multiple ChoiceWhat is the force on an electron with velocity in a region of space with magnetic field ?608views
- Textbook Question
The current in a wire varies with time according to the relationship . What constant current would transport the same charge in the same time interval?
840views - Textbook Question
The current in a wire varies with time according to the relationship . How many coulombs of charge pass a cross section of the wire in the time interval between and ?
1539views1rank - Textbook Question
The total amount of charge in coulombs that has entered a wire at time t is given by the expression Q=4t−t2, where t is in seconds and t≥0. Find an expression for the current in the wire at time .
47views - Textbook Question
The total amount of charge in coulombs that has entered a wire at time t is given by the expression Q=4t−t2, where t is in seconds and t≥0. Graph I versus t for the interval 0≤t≤4 s.
51views