8. Centripetal Forces & Gravitation
Vertical Centripetal Forces
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
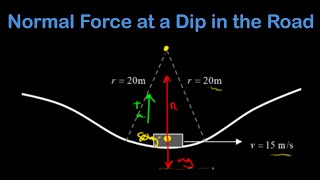
Suppose a 1,800-kg car passes over a bump in a roadway that follows the arc of a circle of radius 20m. What
force does the road exert on the car as the car moves over the top of the bump if the car moves at a constant 9 m/s?2424views26rank4comments - Textbook Question
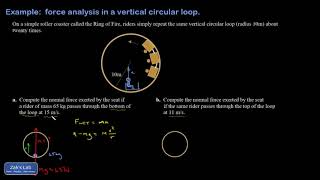
(II) At what minimum speed must a roller coaster be traveling so that passengers upside down at the top of a circle (Fig. 5–45) do not fall out? Assume a radius of curvature of 7.6 m.
<IMAGE>
1085views - Textbook Question
(II) A proposed space station consists of a circular tube that will rotate about its center (like a tubular bicycle tire), Fig. 5–47. The circle formed by the tube has a diameter of about 1.1 km. What must be the rotation speed (revolutions per day) if an effect nearly equal to gravity at the surface of the Earth, 0.90 g, is to be felt by astronauts walking inside? Which part of the tube do they walk on?
898views - Textbook Question
A pilot performs an evasive maneuver by diving vertically at a constant 310 m/s. If he can withstand an acceleration of 9.0 g’s without blacking out, at what altitude must he begin to pull his plane out of the dive (moving in a vertical circular path) to avoid crashing into the sea?
859views - Textbook Question
The physics of circular motion sets an upper limit to the speed of human walking. (If you need to go faster, your gait changes from a walk to a run.) If you take a few steps and watch what's happening, you'll see that your body pivots in circular motion over your forward foot as you bring your rear foot forward for the next step. As you do so, the normal force of the ground on your foot decreases and your body tries to 'lift off' from the ground. A person's center of mass is very near the hips, at the top of the legs. Model a person as a particle of mass m at the top of a leg of length L. Find an expression for the person's maximum walking speed vmax.
1175views