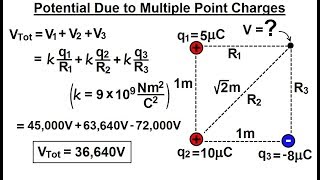
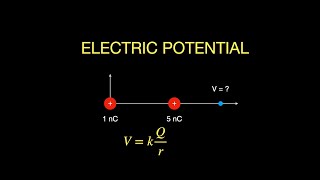
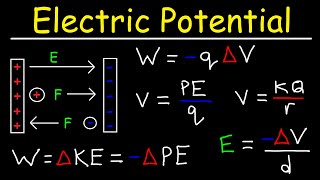
25. Electric Potential
Electric Potential
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
How far from a 5μC charge will the potential be 100 V?
2049views32rank - Multiple Choice
A −1μC and a 5μC charge lie on a line, separated by 5cm. What is the electric potential halfway between the two charges?
2124views39rank8comments - Multiple ChoiceWhat is the electric potential 3.0 cm away from a point charge?1232views
- Multiple ChoiceA charge sits at the origin, and a charge is at . At what location(s) is the potential zero?1154views
- Textbook Question
A thin spherical shell with radius cm is concentric with a larger thin spherical shell with radius cm. Both shells are made of insulating material. The smaller shell has charge nC distributed uniformly over its surface, and the larger shell has charge nC distributed uniformly over its surface. Take the electric potential to be zero at an infinite distance from both shells. What is the electric potential due to the two shells at the following distance from their common center: (i) ; (ii) cm; (iii) cm?
2281views1comments - Textbook Question
Two stationary point charges nC and nC are separated by a distance of cm. An electron is released from rest at a point midway between the two charges and moves along the line connecting the two charges. What is the speed of the electron when it is cm from the -nC charge?
4271views1comments - Textbook Question
How much excess charge must be placed on a copper sphere cm in diameter so that the potential of its center, relative to infinity, is kV? What is the potential of the sphere's surface relative to infinity?
1639views - Textbook Question
Two large, parallel conducting plates carrying opposite charges of equal magnitude are separated by cm. The surface charge density for each plate has magnitude nC/m^2. If the separation between the plates is doubled while the surface charge density is kept constant at the given value, what happens to the magnitude of the electric field and to the potential difference?
1624views