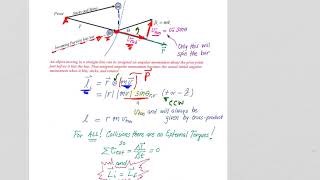
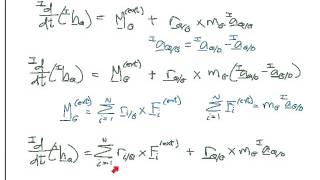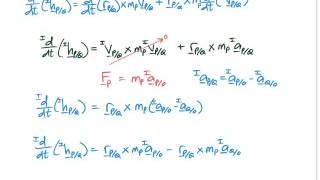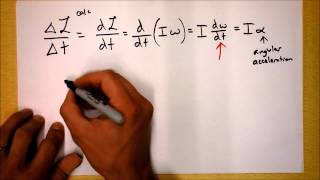16. Angular Momentum
Angular Momentum & Newton's Second Law
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
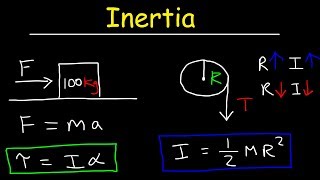
A solid disc of mass M = 40 kg and radius R = 2 m is free to rotate about a fixed, frictionless, perpendicular axis through its center. You apply a constant, tangential force on the disc's surface (as shown), to get it to spin. Calculate the magnitude of the force needed to get the disc to 100 rad/s in just one minute.
1028views2rank2comments - Textbook Question
A 2.00-kg rock has a horizontal velocity of magnitude 12.0 m/s when it is at point P in Fig. E10.35. At this instant, what are the magnitude and direction of its angular momentum relative to point O?
1221views - Textbook Question
A 2.00-kg rock has a horizontal velocity of magnitude 12.0 m/s when it is at point P in Fig. E10.35. If the only force acting on the rock is its weight, what is the rate of change (magnitude and direction) of its angular momentum at this instant?
2266views - Textbook Question
A thin string is wrapped around a cylindrical hoop of radius R and mass M (Fig. 11–46). One end of the string is fixed, and the hoop is allowed to fall vertically, starting from rest, as the string unwinds. Determine the angular momentum of the hoop about its cm as a function of time.
899views - Textbook Question
A thin string is wrapped around a cylindrical hoop of radius R and mass M (Fig. 11–46). One end of the string is fixed, and the hoop is allowed to fall vertically, starting from rest, as the string unwinds. What is the tension in the string as a function of time?
651views - Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements does not use the term angular size or angular distance correctly?
68views - Multiple Choice
What is the angular speed of the tip of the minute hand on a standard clock, in per ?
32views - Multiple Choice
A CD with initial angular velocity is spinning on a frictional surface and comes to rest after a time with constant angular deceleration . How many revolutions does the CD make before stopping?
31views