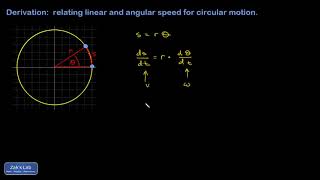
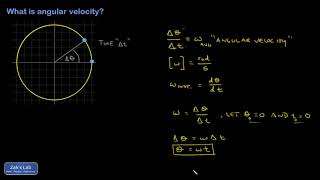
8. Centripetal Forces & Gravitation
Uniform Circular Motion
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
A ball travels on a frictionless circular track at 3m/s. The ball cannot have an acceleration greater than 1.5m/s2 or it will go off the track. What is the smallest radius the circular track can have so that the ball stays on the track?
2509views65rank2comments - Textbook Question
At its Ames Research Center, NASA uses its large '20-G' centrifuge to test the effects of very large accelerations ('hypergravity') on test pilots and astronauts. In this device, an arm 8.84 m long rotates about one end in a horizontal plane, and an astronaut is strapped in at the other end. Suppose that he is aligned along the centrifuge's arm with his head at the outermost end. The maximum sustained acceleration to which humans are subjected in this device is typically 12.5g. What is the difference between the acceleration of his head and feet if the astronaut is 2.00 m tall?
3565views2rank1comments - Textbook Question
At its Ames Research Center, NASA uses its large '20-G' centrifuge to test the effects of very large accelerations ('hypergravity') on test pilots and astronauts. In this device, an arm 8.84 m long rotates about one end in a horizontal plane, and an astronaut is strapped in at the other end. Suppose that he is aligned along the centrifuge's arm with his head at the outermost end. The maximum sustained acceleration to which humans are subjected in this device is typically 12.5g. How fast must the astronaut's head be moving to experience this maximum acceleration?
1648views - Textbook Question
A model of a helicopter rotor has four blades, each 3.40 m long from the central shaft to the blade tip. The model is rotated in a wind tunnel at 550 rev/min. What is the radial acceleration of the blade tip expressed as a multiple of g?
1435views - Textbook Question
A model of a helicopter rotor has four blades, each 3.40 m long from the central shaft to the blade tip. The model is rotated in a wind tunnel at 550 rev/min. What is the linear speed of the blade tip, in m/s?
3380views - Multiple Choice
What is the primary difference between motion along a pathway and motion along a pathway?
779views - Multiple Choice
In the context of uniform circular motion, which term describes a path that is not centered around a common point?
473views - Multiple ChoiceFor an object in a vertical circle, given the radius of the circle, what is the minimum speed required for the object to maintain circular motion at the top of the circle?625views