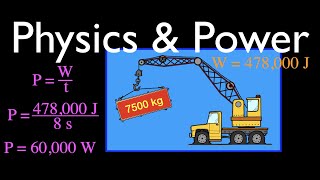
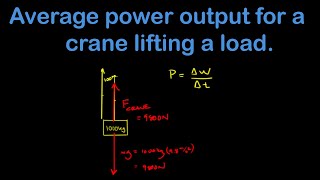
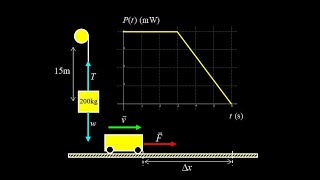
9. Work & Energy
Power
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
How much power must an elevator motor supply in order to lift a 1000 kg elevator at constant speed a height of 100m in 50 seconds?
2176views32rank9comments - Textbook Question
A -kg rock is sliding on a rough, horizontal surface at m/s and eventually stops due to friction. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the rock and the surface is . What average power is produced by friction as the rock stops?
4336views - Textbook Question
An outboard motor for a boat is rated at 35 hp. If it can move a particular boat at a steady speed of 35 km/h, what is the total force resisting the motion of the boat?
1339views - Textbook Question
A driver notices that her 950-kg car, when in neutral, slows down from 95 km/h to 65 km/h in about 7.0 s on a flat horizontal road. Approximately what power (watts and hp) is needed to keep the car traveling at a constant 80 km/h?
1193views - Textbook Question
During a workout, football players ran up the stadium stairs in 75 s. The distance along the stairs is 83 m and they are inclined at a 33° angle. If a player has a mass of 88 kg, estimate his average power output on the way up. Ignore friction and air resistance.
1143views - Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about is true?
1049views - Multiple ChoiceIn a circuit with constant voltage, if the resistance is doubled, how does the power dissipated by the circuit change?1010views
- Multiple ChoiceIf we double the resistance in a circuit but keep the current constant, how will the power dissipated by that circuit change?975views