- 0. Math Review
- 1. Intro to Physics Units
- 2. 1D Motion / Kinematics
- Vectors, Scalars, & Displacement
- Average Velocity
- Intro to Acceleration
- Position-Time Graphs & Velocity
- Conceptual Problems with Position-Time Graphs
- Velocity-Time Graphs & Acceleration
- Calculating Displacement from Velocity-Time Graphs
- Conceptual Problems with Velocity-Time Graphs
- Calculating Change in Velocity from Acceleration-Time Graphs
- Graphing Position, Velocity, and Acceleration Graphs
- Kinematics Equations
- Vertical Motion and Free Fall
- Catch/Overtake Problems
- 3. Vectors
- Review of Vectors vs. Scalars
- Introduction to Vectors
- Adding Vectors Graphically
- Vector Composition & Decomposition
- Adding Vectors by Components
- Trig Review
- Unit Vectors
- Introduction to Dot Product (Scalar Product)
- Calculating Dot Product Using Components
- Intro to Cross Product (Vector Product)
- Calculating Cross Product Using Components
- 4. 2D Kinematics
- 5. Projectile Motion
- 6. Intro to Forces (Dynamics)
- 7. Friction, Inclines, Systems
- 8. Centripetal Forces & Gravitation
- Uniform Circular Motion
- Period and Frequency in Uniform Circular Motion
- Centripetal Forces
- Vertical Centripetal Forces
- Flat Curves
- Banked Curves
- Newton's Law of Gravity
- Gravitational Forces in 2D
- Acceleration Due to Gravity
- Satellite Motion: Intro
- Satellite Motion: Speed & Period
- Geosynchronous Orbits
- Overview of Kepler's Laws
- Kepler's First Law
- Kepler's Third Law
- Kepler's Third Law for Elliptical Orbits
- Gravitational Potential Energy
- Gravitational Potential Energy for Systems of Masses
- Escape Velocity
- Energy of Circular Orbits
- Energy of Elliptical Orbits
- Black Holes
- Gravitational Force Inside the Earth
- Mass Distribution with Calculus
- 9. Work & Energy
- 10. Conservation of Energy
- Intro to Energy Types
- Gravitational Potential Energy
- Intro to Conservation of Energy
- Energy with Non-Conservative Forces
- Springs & Elastic Potential Energy
- Solving Projectile Motion Using Energy
- Motion Along Curved Paths
- Rollercoaster Problems
- Pendulum Problems
- Energy in Connected Objects (Systems)
- Force & Potential Energy
- 11. Momentum & Impulse
- Intro to Momentum
- Intro to Impulse
- Impulse with Variable Forces
- Intro to Conservation of Momentum
- Push-Away Problems
- Types of Collisions
- Completely Inelastic Collisions
- Adding Mass to a Moving System
- Collisions & Motion (Momentum & Energy)
- Ballistic Pendulum
- Collisions with Springs
- Elastic Collisions
- How to Identify the Type of Collision
- Intro to Center of Mass
- 12. Rotational Kinematics
- 13. Rotational Inertia & Energy
- More Conservation of Energy Problems
- Conservation of Energy in Rolling Motion
- Parallel Axis Theorem
- Intro to Moment of Inertia
- Moment of Inertia via Integration
- Moment of Inertia of Systems
- Moment of Inertia & Mass Distribution
- Intro to Rotational Kinetic Energy
- Energy of Rolling Motion
- Types of Motion & Energy
- Conservation of Energy with Rotation
- Torque with Kinematic Equations
- Rotational Dynamics with Two Motions
- Rotational Dynamics of Rolling Motion
- 14. Torque & Rotational Dynamics
- 15. Rotational Equilibrium
- 16. Angular Momentum
- Opening/Closing Arms on Rotating Stool
- Conservation of Angular Momentum
- Angular Momentum & Newton's Second Law
- Intro to Angular Collisions
- Jumping Into/Out of Moving Disc
- Spinning on String of Variable Length
- Angular Collisions with Linear Motion
- Intro to Angular Momentum
- Angular Momentum of a Point Mass
- Angular Momentum of Objects in Linear Motion
- 17. Periodic Motion
- 18. Waves & Sound
- 19. Fluid Mechanics
- 20. Heat and Temperature
- Temperature
- Linear Thermal Expansion
- Volume Thermal Expansion
- Moles and Avogadro's Number
- Specific Heat & Temperature Changes
- Latent Heat & Phase Changes
- Intro to Calorimetry
- Calorimetry with Temperature and Phase Changes
- Advanced Calorimetry: Equilibrium Temperature with Phase Changes
- Phase Diagrams, Triple Points and Critical Points
- Heat Transfer
- 21. Kinetic Theory of Ideal Gases
- 22. The First Law of Thermodynamics
- 23. The Second Law of Thermodynamics
- 24. Electric Force & Field; Gauss' Law
- 25. Electric Potential
- 26. Capacitors & Dielectrics
- 27. Resistors & DC Circuits
- 28. Magnetic Fields and Forces
- 29. Sources of Magnetic Field
- 30. Induction and Inductance
- 31. Alternating Current
- 32. Electromagnetic Waves
- 33. Geometric Optics
- 34. Wave Optics
- 35. Special Relativity
22. The First Law of Thermodynamics
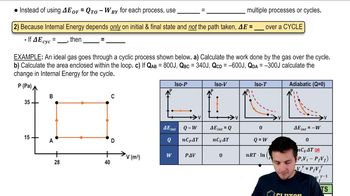
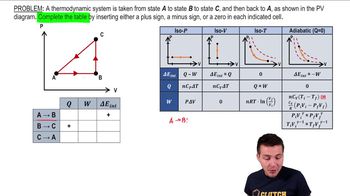
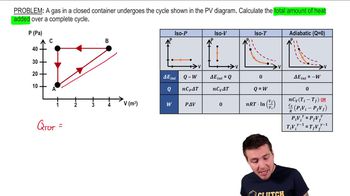
Cyclic Thermodynamic Processes
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
An ideal gas is taken through the four processes shown below. The changes in internal energy for three of these processes are as follows: ΔEAB = +82 J; ΔEBC = +15 J; ΔEDA =–56 J. Find the change in internal energy for the process from C to D.
1514views3rank - Textbook Question
0.25 mol of a gas are compressed at a constant pressure of 250 kPa from 6000 cm3 to 2000 cm3, then expanded at a constant temperature back to 6000 cm3. What is the net work done on the gas?
908views - Textbook Question
A gas following the pV trajectory of FIGURE EX21.11 does 60 J of work per cycle. What is Vmax?
225views - Textbook Question
A heat engine using a diatomic gas follows the cycle shown in FIGURE P21.55. Its temperature at point 1 is 20℃. Determine Ws, Q, and ∆Eth for each of the three processes in this cycle. Display your results in a table.
888views - Textbook Question
A heat engine uses a diatomic gas that follows the pV cycle in FIGURE P21.59. Determine the pressure, volume, and temperature at point 2.
155views