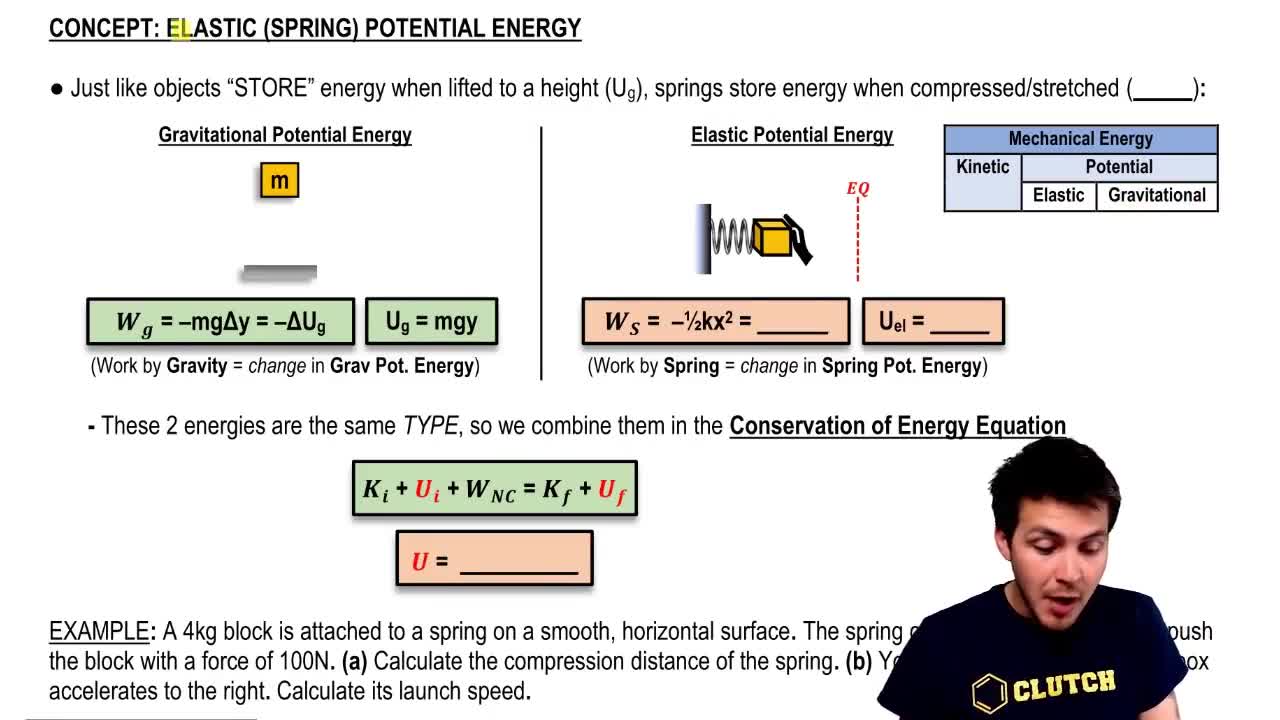
10. Conservation of Energy
Springs & Elastic Potential Energy
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
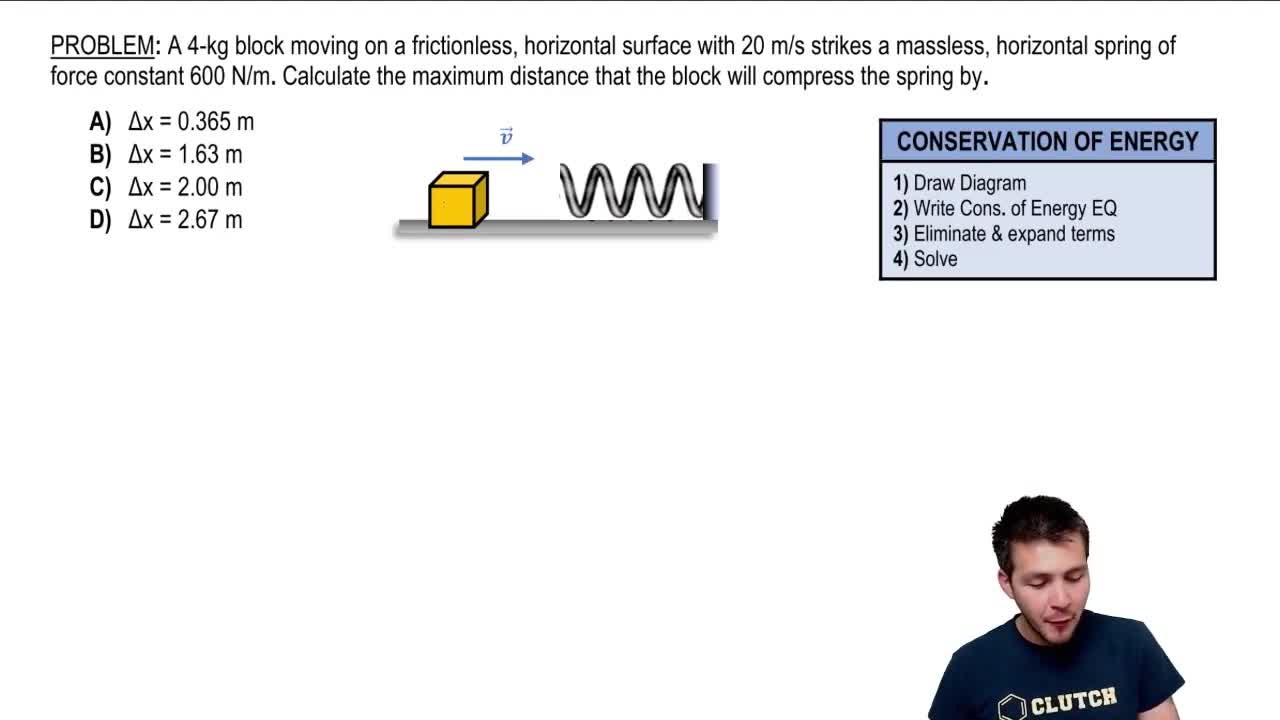
A 4-kg block moving on a flat surface strikes a massless, horizontal spring of force constant 600 N/m with a 20 m/s. The block-surface coefficient of friction is 0.5. Calculate the maximum compression that the spring will experience.
1352views27rank6comments - Textbook Question
A spring of negligible mass has force constant N/m. You place the spring vertically with one end on the floor. You then drop a -kg book onto it from a height of m above the top of the spring. Find the maximum distance the spring will be compressed.
2928views - Textbook Question
A spring of negligible mass has force constant N/m. How far must the spring be compressed for J of potential energy to be stored in it?
2186views1rank - Textbook Question
A spring of negligible mass has force constant N/m. How far must the spring be compressed for J of potential energy to be stored in it?
1039views - Textbook Question
A spring has a spring constant k of 78.0 N/m. How much must this spring be compressed to store 45.0 J of potential energy?
411views - Multiple Choice
When a spring is stretched by an external force and held at a fixed length, does the spring possess elastic potential energy?
42views - Multiple Choice
Which of the following scenarios generates the most elastic potential energy in a spring with spring constant and equilibrium length, assuming the same spring is used in each case?
37views - Multiple Choice
For a spring obeying Hooke's law, doubling which of the following quantities would cause the largest increase in the spring's elastic potential energy ?
17views