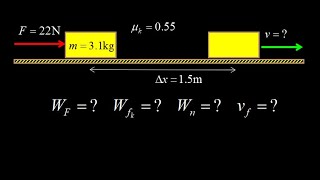
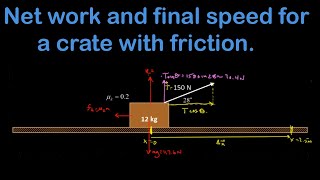
9. Work & Energy
Net Work & Work-Energy Theorem
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
You pull a 3kg box on a flat surface. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.6. When you pull the box horizontally through a distance of 10m, it accelerates at 2m/s2. Find the net work on the box.
2961views43rank9comments - Multiple Choice
To pull a 51 kg crate across a rough floor, a worker applies a force of 100 N, directed 37°above the horizontal. The coefficient of friction is 0.16. If the crate moves 3.0 m, what is the total work done on the crate?
2633views32rank8comments - Multiple Choice
A box slides across the floor with an initial speed of 3.5m/s. If the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.15, how far will the box slide before stopping completely?
2631views40rank - Multiple ChoiceRhys gave a crate a shove across a horizontal floor. When the crate left his hands, it was moving . If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the floor is 0.32, how far will the crate slide? Use energy concepts to solve this problem.1243views1rank
- Textbook Question
You throw a -N rock vertically into the air from ground level. You observe that when it is m above the ground, it is traveling at m/s upward. Use the work–energy theorem to find its maximum height.
1914views - Textbook Question
A -kg book is sliding along a rough horizontal surface. At point it is moving at m/s, and at point it has slowed to m/s. How much work was done on the book between and ?
2604views - Textbook Question
You throw a -N rock vertically into the air from ground level. You observe that when it is m above the ground, it is traveling at m/s upward. Use the work–energy theorem to find the rock's speed just as it left the ground.
6443views9rank - Textbook Question
(II) An 85-g arrow is fired from a bow whose string exerts an average force of 105 N on the arrow over a distance of 75 cm. What is the speed of the arrow as it leaves the bow?
1182views