What is the significance of
(b) Dalton's law, to the process of respiration?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: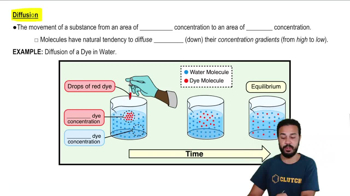

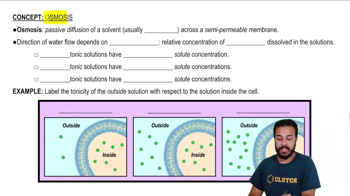

 6:12m
6:12mMaster Partial Pressure with a bite sized video explanation from Bruce Bryan
Start learning