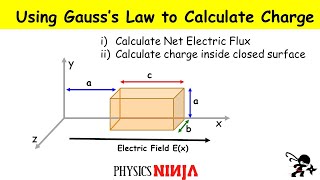
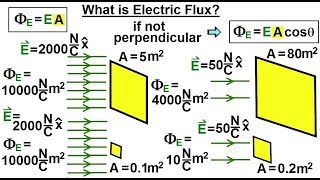
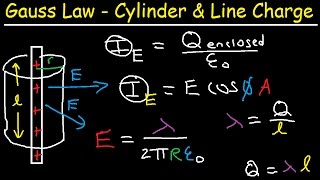
24. Electric Force & Field; Gauss' Law
Gauss' Law
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Rank the flux through surfaces A, B and C in the figure below from greatest to smallest.
1472views35rank3comments - Multiple Choice
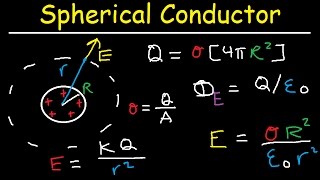
A spherical, thin conducting shell of radius 8cm has a charge of –6C. If a 4C charge were placed at the center of the shell, what is the electric field 4 cm from the center? At 12 cm?
1616views23rank7comments - Multiple ChoiceA cube has sides equal to . The net flux through the cube is outward. Is the net charge in the cube positive, negative or zero?892views
- Multiple ChoiceAn electric field with strength exists just outside a face of a large block of aluminum. If the electric field points towards the block, what is the surface charge density on the face of the block?824views
- Textbook Question
The nuclei of large atoms, such as uranium, with protons, can be modeled as spherically symmetric spheres of charge. The radius of the uranium nucleus is approximately m. The electrons can be modeled as forming a uniform shell of negative charge. What net electric field do they produce at the location of the nucleus?
2158views - Textbook Question
The nuclei of large atoms, such as uranium, with protons, can be modeled as spherically symmetric spheres of charge. The radius of the uranium nucleus is approximately m. What is the electric field this nucleus produces just outside its surface?
752views1rank - Textbook Question
Some planetary scientists have suggested that the planet Mars has an electric field somewhat similar to that of the earth, producing a net electric flux of Nm2/C at the planet's surface. Calculate the charge density on Mars, assuming all the charge is uniformly distributed over the planet's surface.
627views1rank - Textbook Question
Some planetary scientists have suggested that the planet Mars has an electric field somewhat similar to that of the earth, producing a net electric flux of Nm2/C at the planet's surface. Calculate the electric field at the planet's surface (refer to the astronomical data inside the back cover).
1263views