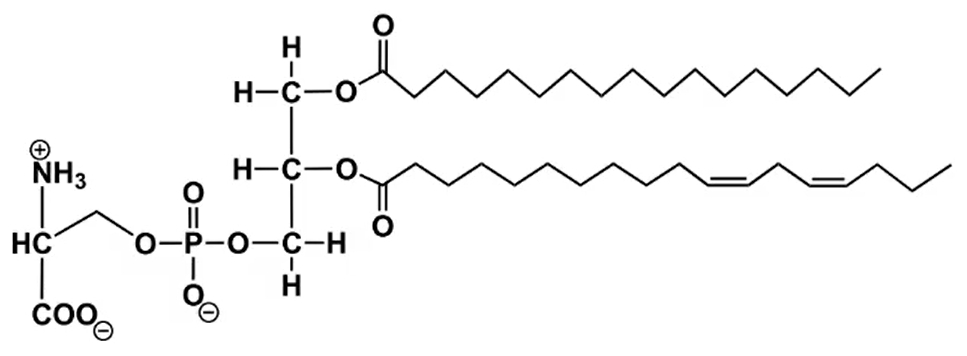
Glycerophospholipids are a specific type of phospholipid, which are essential components of cell membranes. To understand glycerophospholipids, it's important to first grasp the broader category of phospholipids. Phospholipids are lipids that contain at least one phosphate group, making them crucial for cellular structure and function.
These molecules are characterized by their fatty acid base, meaning they include at least one fatty acid chain linked to a phosphorylated platform molecule. The general structure of a phospholipid consists of a platform molecule, which can vary, and one or more fatty acid chains. When the platform molecule is glycerol, the resulting structure is classified as a glycerophospholipid.
In the context of cell membranes, phospholipids play a vital role due to their amphipathic nature, which allows them to form bilayers that create a barrier between the interior of the cell and the external environment. This bilayer structure is fundamental to maintaining cellular integrity and facilitating communication and transport across membranes.
In summary, glycerophospholipids are a subtype of phospholipids that specifically utilize glycerol as their platform molecule. Understanding their structure and function is key to comprehending the complexities of cell membranes and their roles in biological systems.