13. Mendelian Genetics
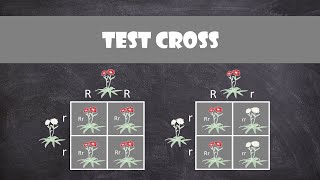
Test Crosses
13. Mendelian Genetics
Test Crosses
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
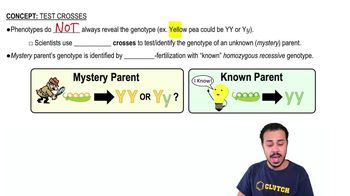
A single gene test cross is conducted to determine the genotype of a pea plant that shows the dominant phenotype for height (T = tall, t = short). If all offspring of the cross show the dominant phenotype, then the genotype of the unknown parent is _______.
4006views15rank2comments - Multiple Choice
You want to determine the pea color genotype of a pea plant with yellow peas. You conduct a test cross with your mystery pea plant. The test cross results in 50% of the offspring possessing yellow peas and 50% of the offspring possessing green peas. What is the genotype for pea color of the mystery parent?
2799views23rank - Multiple ChoiceWhat is indicated when a single-character testcross yields offspring that all have the dominant phenotype?1718views
- Multiple ChoiceA gray-bodied, vestigial-winged fly is crossed with a black-bodied, normal-winged fly. The F1 progeny is testcrossed. Among the resulting offspring, __________ is a parental type, and __________ is a recombinant type.1904views1rank