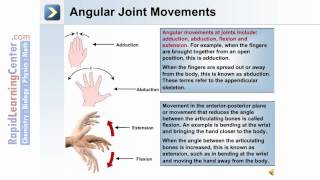
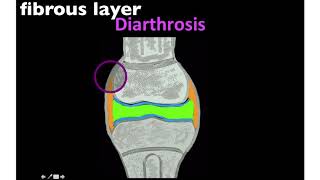
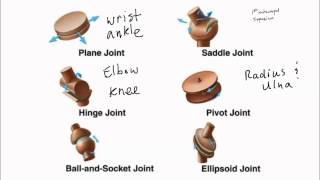
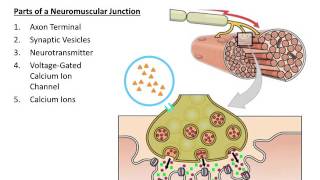
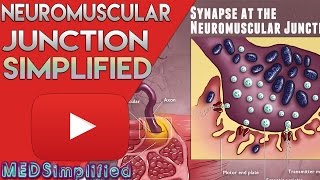
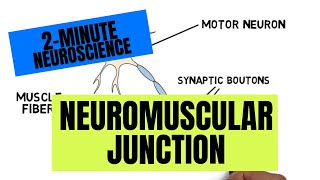
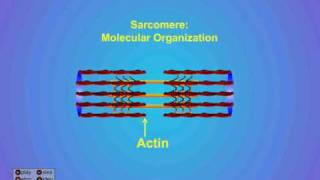
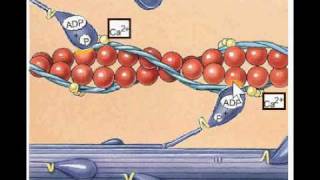
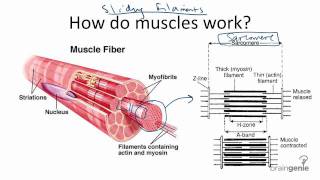
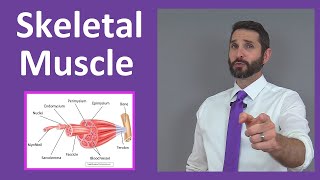
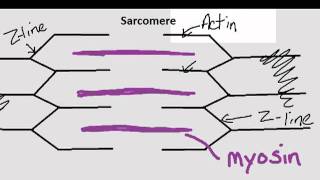
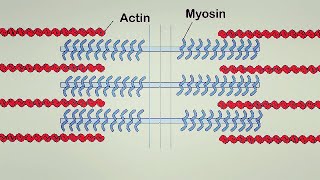
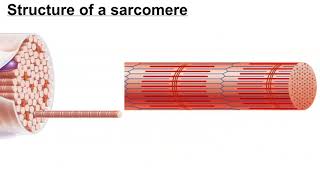
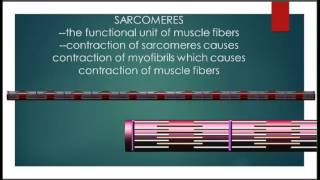
47. Muscle Systems
Musculoskeletal System
47. Muscle Systems
Musculoskeletal System
Showing 7 of 7 videos
Additional 42 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 45 of 45 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceWhat type of muscle is striated with intercalated disks?1385views
- Multiple ChoiceWhich statement about muscle contraction is correct?1398views
- Multiple ChoiceWhat do all muscle tissues have in common?1917views
- Multiple ChoiceWhy is having a hydrostatic skeleton rather than an internal skeleton advantageous to an earthworm?1431views