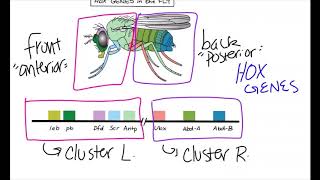
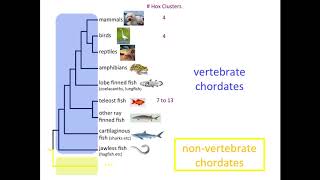
20. Development
Developmental Biology
20. Development
Developmental Biology
Showing 5 of 5 videos
Additional 39 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 42 of 42 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceCytoplasmic determinants __________.2507views
- Multiple ChoiceCells can influence each other's development by a process known as __________.1288views1rank
- Multiple ChoiceInstead of developing a head and a tail, an abnormal Drosophila embryo develops two tails. This is most likely due to __________.1472views
- Multiple ChoiceCell differentiation is first observable when __________.1728views





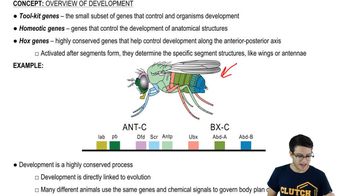






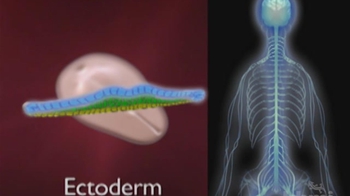

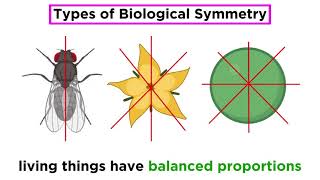






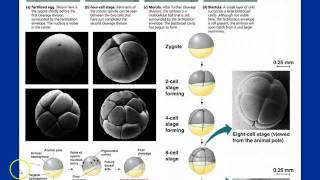

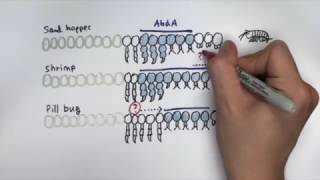
![Drosophila Embryogenesis - Anterior/Posterior Patterning [English Captions]](https://img.youtube.com/vi/ZOzKXrOGtgw/mqdefault.jpg)