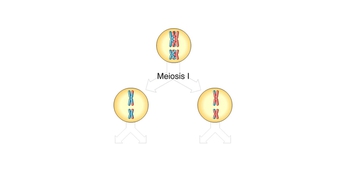
12. Meiosis
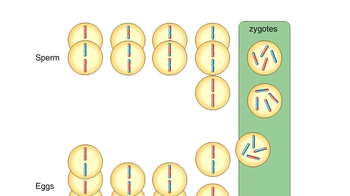
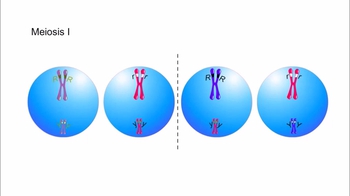
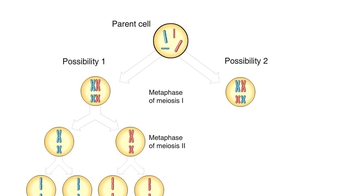
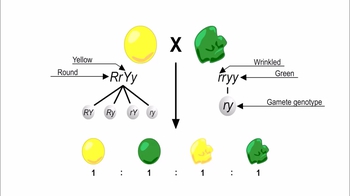
Genetic Variation During Meiosis
12. Meiosis
Genetic Variation During Meiosis
Additional 7 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 10 of 10 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes occurs when homologous chromosomes cross over in meiosis I?
4376views39rank - Multiple Choice
Crossing over involves each of the following EXCEPT:
3408views30rank1comments - Multiple Choice
How many genetically unique gametes can be created in an organism with 4 chromosomes?
4976views14rank8comments - Multiple Choice
During which of the following processes does independent assortment of chromosomes occur?
4195views18rank